Fatigue Performance of Titanium Alloy Centrifugal Impeller Under Multi-processing State
-
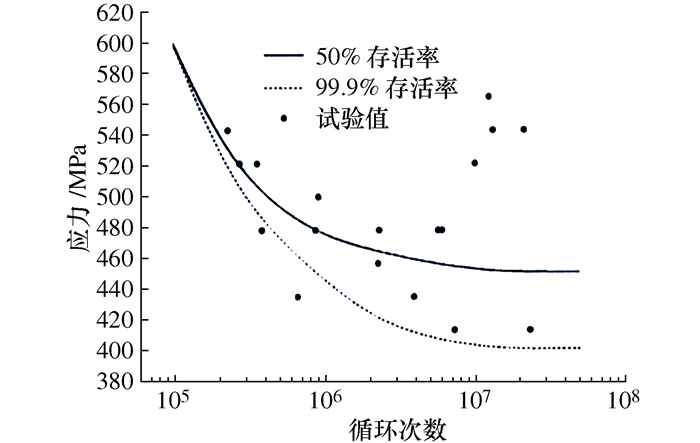
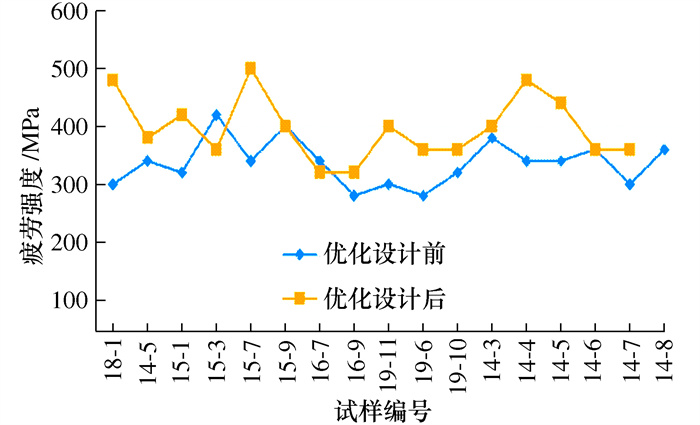
摘要: 离心叶轮叶片的疲劳强度是叶轮叶片表面完整性各特征量的综合作用结果, 不同工艺参数的叶片表面完整性状态也不相同, 带来不同的疲劳特性。本文重点研究精密切削和喷丸强化对钛合金(TC11)离心叶轮叶片疲劳特性的影响规律, 根据不同工艺状态下叶轮叶片疲劳强度试验反馈数据, 开展基于离心叶轮结构特征的形性优化设计, 并通过振动疲劳试验, 采集循环次数3×107的叶轮叶片疲劳强度值, 试验结果表明优化设计后的叶轮叶片疲劳强度提升15%, 对新研型号的离心叶轮加工参数优化和结构设计优化具有重要指导意义。Abstract: The fatigue strength of centrifugal impeller is the result of the combined influence of the various characteristic quantities on the blade surface integrity. Different processing parameters lead to distinct states of blade surface integrity, resulting in various fatigue performance. the effects of the precision cutting and shot peening on the fatigue performance of TC11 centrifugal impeller blades is focused. By analyzing the fatigue strength data under different processing conditions of the blade, the impeller's structural features have been optimized and designed. The results show that the fatigue strength of the optimized impeller blade increased approximate 15% under the high-frequency fatigue testing at a cycle number of 3×107, which has an important guidance for optimizing the processing parameters and structural design of the new type centrifugal impeller.
-
表 1 铣削状态下的叶轮工艺参数
Table 1. Milling parameters of TC11 centrifugal impellers
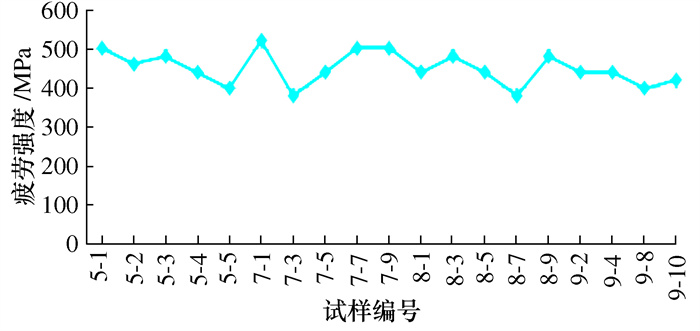
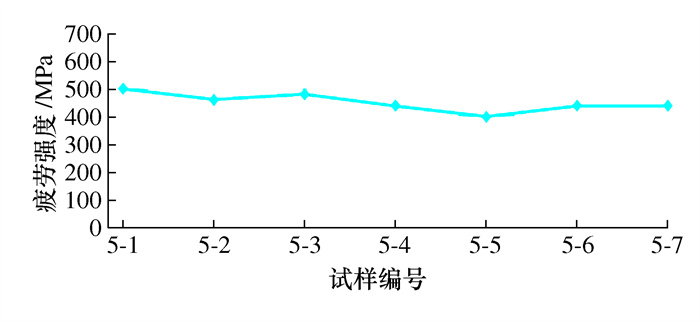
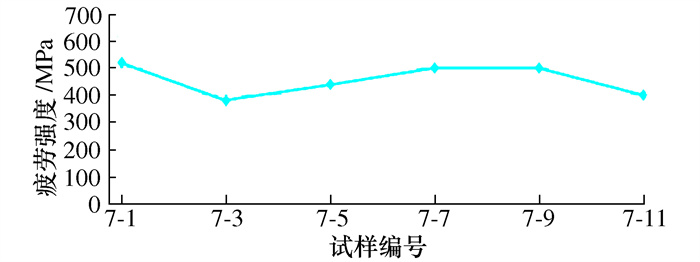
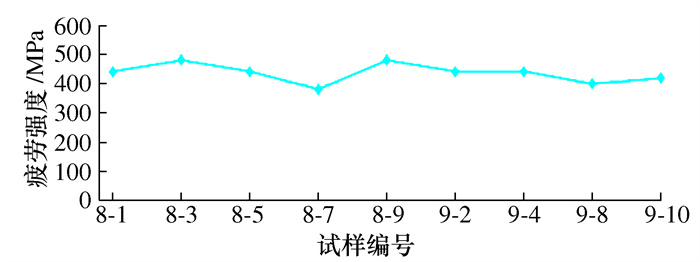
叶片序号 切削速度/ (m·min-1) 每齿进给/ (mm·z-1) 行距/ mm 粗糙度等级/μm 冷却液 5-1~5-11 9-1~9-4 80 0.1 0.3 1.2 水基 7-1~7-11 9-5~9-8 80 0.1 0.2 0.8 水基 8-1~8-11 9-9~9-11 80 0.1 0.16 0.6 水基 表 2 铣削状态下叶轮叶片疲劳实验结果
Table 2. Fatigue test results of impeller blades in milling state
编号 1阶频率 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 5-1 2 526.9 叶盆 280 500 20 2.142 6 13 641 350 y=233.91x-1.173 5, R2=0.997 8 5-2 2 488.9 边缘-长边 380 460 20 2.249 5 915 071 y=204.06x+0.975 3, R2=0.999 3 5-3 2 547.5 叶背 280 480 20 2.307 3 275 335 y=206.88x+2.674 9, R2=0.999 8 5-4 2 532.0 叶背 400 440 20 2.165 5 385 218 y=201.99x+2.586 7, R2=0.998 4 5-5 2 550.1 叶背 380 400 20 2.061 8 661 621 y=193.37x+1.313, R2=0.998 4 7-1 2 552.0 边缘-长边 400 520 20 2.452 0 12 786 160 y=210.04x+4.975, R2=0.997 9 7-3 2 540.0 边缘-长边 300 380 20 2.330 7 7 237 254 y=160.99x+4.773 7, R2=0.999 1 7-5 2 545.8 边缘-长边 380 440 20 2.107 3 2 306 580 y=208.26x+1.143, R2=0.999 0 7-7 2 564.0 边缘-长边 400 500 20 2.083 2 21 911 882 y=242.31x-4.772 7, R2=0.996 1 7-9 2 536.8 边缘-长边 380 500 20 2.417 1 230 431 y=206.64x+0.553, R2=0.997 0 8-1 2 522.8 边缘-长边 380 440 20 2.231 2 873 126 y=194.36x+6.350 1, R2=0.999 4 8-3 2 541.1 边缘-长边 380 480 20 2.343 0 10 037 924 y=202.68x+5.125 1, R2=0.999 9 8-5 2 534.6 叶背 360 440 20 2.276 8 5 684 801 y=192.61x+2.872 2, R2=0.999 1 8-7 2 533.0 叶背 360 380 20 2.142 9 23 488 453 y=175.33x+4.289 9, R2=0.999 7 8-9 2 534.0 边缘-长边 360 480 20 2.445 8 360 439 y=199.23x-7.284 2, R2=0.999 6 9-2 2 535.8 边缘-长边 340 440 20 2.483 2 6 031 455 y=175.21x+4.920 3, R2=0.999 1 9-4 2 546.1 边缘-长边 340 440 20 2.4 385 459 y=180.82x+6.024 6, R2=0.999 7 9-6 2 533.3 叶背 20 位移递增至1.4 mm左右样品便已损坏 y=186.57x+5.073 1, R2=0.999 3 9-8 2 549.0 叶背 380 400 20 2.065 2 3 893 741 y=190.91x+5.742 2, R2=0.997 7 9-10 2 514.6 边缘-长边 340 420 20 2.317 3 2 261 057 y=178.94x+5.340 2, R2=0.999 6 表 3 喷丸强度0.10 N, 粗糙度Ra=0.8的叶轮疲劳实验结果
Table 3. Fatigue test results of impeller blades with toughness Ra=0.8 and peening strength of 0.10 N
编号 共振频率/Hz 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 14-1 2 522.0 边缘-长边 280 340 20 1.723 7 26 013 544 y=201.42x-7.195 1,R2=0.997 9 14-3 2 532.2 边缘-长边 280 400 20 1.720 1 8 358 912 y=240.24x-14.914,R2=0.999 2 14-5 2 527.5 边缘-长边 260 380 20 2.289 3 26 772 870 y=164.23x+4.034 4,R2=0.999 1 14-7 2 523.3 边缘-长边 240 340 20 2.105 2 9 394 406 y=160.32x+2.491 1,R2=0.999 6 15-1 2 535.0 边缘-长边 280 420 20 2.325 2 27 946 414 y=178.76x+4.353 2,R2=0.999 2 15-3 2 536.0 边缘-长边 280 360 20 1.907 0 770 021 y=187.25x+2.922 2,R2=0.998 8 15-5 2 534.7 边缘-长边 240 280 20 1.814 1 1 689 004 y=154.02x+0.588 3,R2=0.998 0 15-7 2 540.0 边缘-长边 320 500 20 2.274 9 9 346 642 y=219.46x+0.753 6,R2=0.999 8 15-9 2 520.0 边缘-长边 280 400 20 2.013 8 9 980 728 y=196.68x+3.931 4,R2=0.999 9 表 4 喷丸强度0.15 N, 粗糙度Ra=0.8的叶轮疲劳实验结果
Table 4. Fatigue test results of impeller blades with toughness Ra=0.8 amd peening strength of 0.15 N
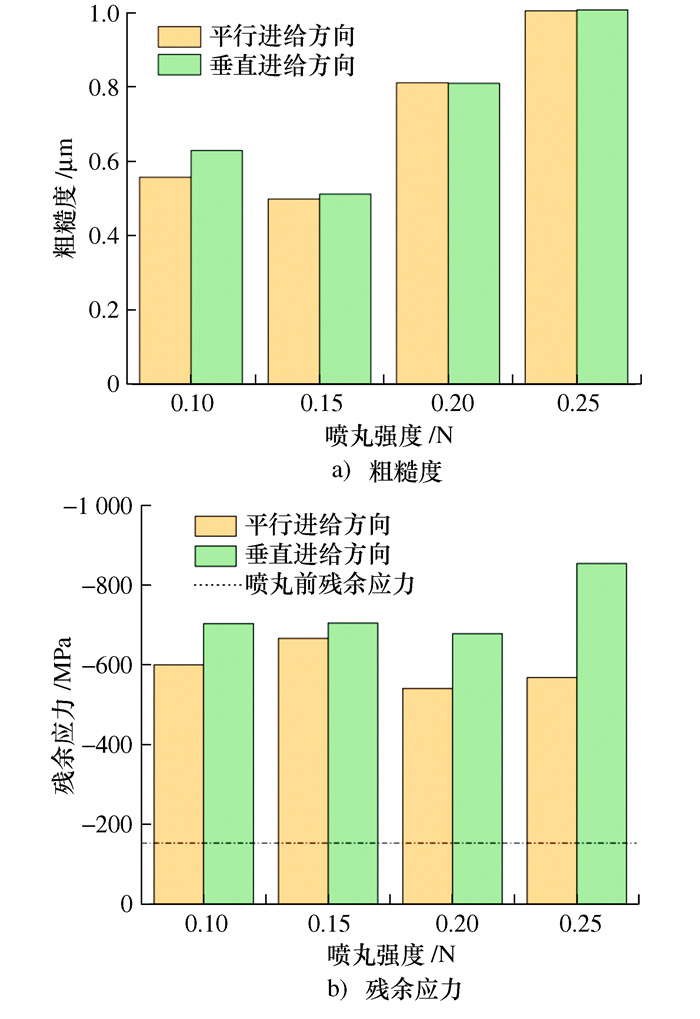
编号 共振频率/Hz 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 13-1 2 541.3 边缘-长边 280 300 20 1.627 5 21 730 062 y=178.09x+10.161,R2=0.997 1 13-3 2 512.0 边缘-长边 280 340 20 1.704 8 8 148 103 y=198.92x+0.890 3,R2=0.999 3 13-5 2 512.2 边缘-长边 300 320 20 1.812 5 5 653 211 y=174.28x+4.122 6,R2=0.999 6 13-7 2 537.0 边缘-长边 300 480 20 2.361 2 8 192 425 y=202.92x+0.870 3,R2=0.999 1 13-9 2 534.0 边缘-长边 300 420 20 1.751 7 6 383 446 y=236.75x+5.291 1,R2=0.996 7 19-6 2 505.5 边缘-长边 260 360 20 1.739 2 17 754 648 y=204.3x+4.684 5,R2=0.996 3 19-8 2 512.7 边缘-长边 240 300 20 1.383 5 23 912 913 y=215.1x+2.402 7,R2=0.999 3 表 5 喷丸强度0.20 N, 粗糙度Ra=0.8的叶轮疲劳实验结果
Table 5. Fatigue test results of impeller blades with toughness Ra=0.8 and peening strength of 0.20 N
编号 共振频率/Hz 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 16-1 2 534.0 边缘-长边 280 300 20 1.462 2 16 891 901 y=203.86x+1.925 5,R2=0.998 2 16-3 2 541.4 边缘-长边 240 280 20 1.443 6 8 751 164 y=193.28x+0.978 2,R2=0.999 16-5 2 536.9 边缘-长边 280 320 20 1.591 4 18 554 402 y=200.86x+0.361 4,R2=0.998 5 16-7 2 529.0 边缘-长边 300 380 20 1.629 9 25 314 299 y=234.77x-2.65,R2=0.999 6 16-9 2 506.2 边缘-长边 260 320 20 1.712 7 12 612 076 y=186.31x+0.908 1,R2=0.996 4 19-2 2 535.8 边缘-长边 280 340 20 1.653 2 22 442 029 y=205.46x+0.322 4,R2=0.999 19-4 20 y=153.91x+3.085 5,R2=0.997 1 表 6 喷丸强度0.25 N, 粗糙度Ra=0.8的叶轮疲劳实验结果
Table 6. Fatigue test results of impeller blades with toughness Ra=0.8 and peening strength of 0.25 N
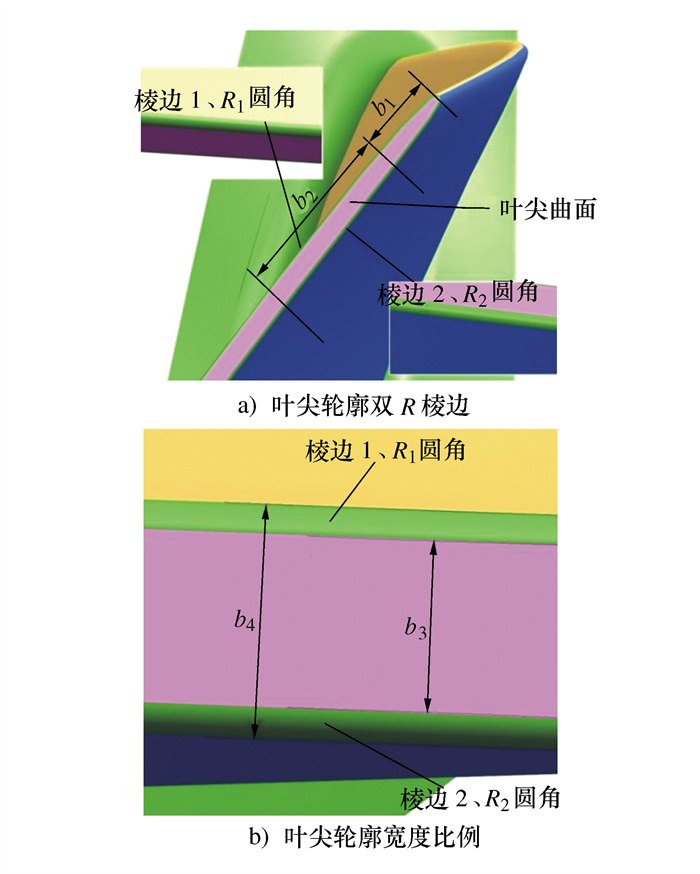
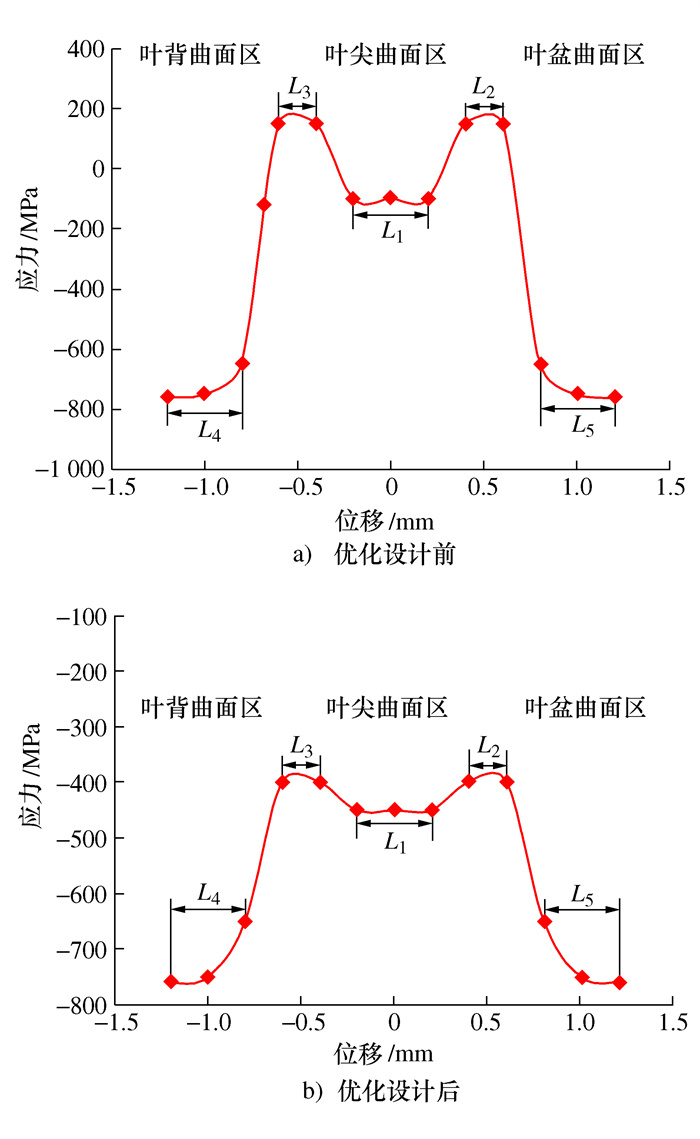
编号 共振频率/Hz 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 17-1 2 524.8 边缘-长边 300 320 20 1.612 5 18 984 455 y=197.47x+1.585 5,R2=0.998 8 17-3 2 525.5 边缘-长边 320 400 20 1.992 6 1 715 767 y=200.66x+0.164 7,R2=0.998 4 17-5 2 540.7 边缘-长边 300 360 20 1.830 7 9 257 839 y=198.58x-3.547 3,R2=0.999 3 17-7 2 538.0 边缘-长边 300 360 20 1.828 9 608 912 y=197.83x-1.806 7,R2=0.999 6 17-9 2 515.6 边缘-长边 320 400 20 1.777 2 16 822 696 y=226.7x-2.882 4,R2=0.997 8 18-1 2 556.9 边缘-长边 300 480 20 2.266 9 969 331 y=201.95x+2.202 6,R2=0.998 7 18-3 2 548.7 边缘-长边 340 440 20 1.922 2 2 439 227 y=238.95x-19.31,R2=0.999 0 18-5 2 540.4 边缘-长边 320 360 20 1.731 6 11 231 149 y=207.66x-0.423 7,R2=0.999 7 18-7 2 525.9 边缘-长边 320 360 20 1.633 4 4 371 223 y=192.78x+4.456,R2=0.999 3 18-9 2 525.7 边缘-长边 320 340 20 1.569 0 23 017 527 y=218.76x-3.236 8,R2=0.998 7 表 7 叶尖优化设计后叶片疲劳实验结果
Table 7. Fatigue test results of impeller blade after blade tip optimization
编号 共振频率/Hz 破坏位置 初始应力/MPa 最大破坏应力/MPa 应力梯度/MPa 最大破坏应力位移/mm 最大应力破坏循坏次数 线性关系/斜率 18-1 2 556.9 边缘-长边 300 480 20 2.266 9 969 331 y=201.95x+2.202 6, R2=0.998 7 18-3 2 548.7 边缘-长边 340 440 20 1.922 2 2 439 227 y=238.95x-19.31, R2=0.999 0 13-7 2 537.0 边缘-长边 300 480 20 2.361 2 8 192 425 y=202.92x+0.870 3, R2=0.999 1 14-5 2 527.5 边缘-长边 260 380 20 2.289 3 26 772 870 y=164.23x+4.034 4, R2=0.999 1 15-1 2 535.0 边缘-长边 280 420 20 2.325 2 27 946 414 y=178.76x+4.353 2, R2=0.999 2 15-3 2 536.0 边缘-长边 280 360 20 1.907 0 770 021 y=187.25x+2.922 2, R2=0.998 8 15-7 2540.0 边缘-长边 320 500 20 2.274 9 9 346 642 y=219.46x+0.753 6, R2=0.999 8 15-9 2 520.0 边缘-长边 280 400 20 2.013 8 9 980 728 y=196.68x+3.931 4, R2=0.999 9 16-9 2 506.2 边缘-长边 260 320 20 1.712 7 12 612 076 y=186.31x+0.908 1, R2=0.996 4 19-6 2 505.5 边缘-长边 260 360 20 1.739 2 17 754 648 y=204.3x+4.684 5, R2=0.996 3 19-10 2 529.5 边缘-长边 240 360 20 1.723 7 14 393 021 y=211.61x-4.753 5, R2=0.997 8 16-5 2 536.9 边缘-长边 280 320 20 1.591 4 18 554 402 y=200.86x+0.361 4, R2=0.998 5 14-3 2 532.2 边缘-长边 280 400 20 1.720 1 8 358 912 y=240.24x-14.914, R2=0.999 2 -
[1] 王欣, 罗学昆, 宇波, 等. 航空航天用钛合金表面工程技术研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2022, 65(4): 14-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKGJ202204001.htmWANG X, LUO X K, YU B, et al. Research progress on surface engineering technology of aerospace titanium alloys[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 65(4): 14-24. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKGJ202204001.htm [2] 沈雪红, 张定华, 姚倡锋, 等. 钛合金切削加工表面完整性形成机制研究进展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2021, 41(4): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB202104002.htmSHEN X H, ZHANG D H, YAO C F, et al. Research progress on formation mechanism of surface integrity in titanium alloy machining[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2021, 41(4): 1-16. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB202104002.htm [3] ZHAO S H, YUAN K B, GUO W G, et al. A comparative study of laser metal deposited and forged Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Uniaxial mechanical response and vibration fatigue properties[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2020, 136: 105629. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105629 [4] 沈号伦, 王晨羽, 李金泉. 钛合金切削过程进给量对疲劳寿命的影响规律研究[J]. 工具技术, 2022, 56(8): 35-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJJS202208006.htmSHEN H L, WANG C Y, LI J Q. Study on effect of feed on fatigue life in cutting titanium alloy process[J]. Tool Engineering, 2022, 56(8): 35-39. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJJS202208006.htm [5] 季文彬, 邓日清, 戴士杰, 等. 铣削对SLM增材TC4钛合金表面完整性和疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国机械工程, 2023, 34(2): 208-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJX202302011.htmJI W B, DENG R Q, DAI S J, et al. Effects of milling on surface integrity and fatigue performance of TC4 titanium alloy by SLM[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 34(2): 208-217. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJX202302011.htm [6] YANG D, LIU Z Q, XIAO X, et al. The effects of machining-induced surface topography on fatigue performance of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2018, 71: 27-30. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2018.05.015 [7] CHILDERHOUSE T, M'SAOUBI R, FRANCA L, et al. The influence of machining induced surface integrity and residual stress on the fatigue performance of Ti-6Al-4V following polycrystalline diamond and coated cemented carbide milling[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2022, 163: 107054. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.107054 [8] 卜嘉利, 吕扬, 刘博志, 等. 不同喷丸强度对TC17钛合金抗疲劳性能影响[J]. 航空动力学报, 2022, 37(6): 1225-1233. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDI202206010.htmBU J L, LYU Y, LIU B Z, et al. Effect of different shot peening intensities on fatigue resistance of TC17 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2022, 37(6): 1225-1233. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDI202206010.htm [9] 常帅, 谈建平, 张剑睿, 等. 加工残余应力对Ti-6Al-4V试样高周动疲劳性能的影响[J]. 压力容器, 2021, 38(8): 7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLRQ202108002.htmCHANG S, TAN J P, ZHANG J R, et al. Effect of machining residual stress on high cycle fatigue property of Ti-6Al-4V specimens[J]. Pressure Vessel Technology, 2021, 38(8): 7-13. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLRQ202108002.htm [10] 何卫锋, 李应红, 李启鹏, 等. LSP提高TC6钛合金振动疲劳性能及强化机理研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(8): 1643-1648. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201308021.htmHE W F, LI Y H, LI Q P, et al. Vibration fatigue performance and strengthening mechanism of TC6 titanium alloy by laser shock peening[J]. Rare Metal materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(8): 1643-1648. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201308021.htm [11] 易湘斌, 芮执元, 李宝栋, 等. 不同冷却润滑条件下TB6钛合金高速切削表面完整性研究[J]. 润滑与密封, 2018, 43(11): 36-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RHMF201811012.htmYI X B, RUI Z Y, LI B D, et al. Research on TB6 high speed machining surface integrity under different cooling lubricating conditions[J]. Lubrication Engineering, 2018, 43(11): 36-41. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RHMF201811012.htm [12] 张桂冠, 孙玉利, 范武林, 等. 钛合金加工表面完整性的研究现状与展望[J]. 航空制造技术, 2022, 65(4): 36-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKGJ202204003.htmZHANG G G, SUN Y L, FAN W L, et al. Research progress and future development of surface integrity on machined surface of titanium alloys[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 65(4): 36-55. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKGJ202204003.htm [13] 王仁智. 喷丸强化技术在我国的发展[J]. 材料工程, 1989(1): 4-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLGC198901003.htmWANG R Z. The development of shot peening technique in our country[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 1989(1): 4-7. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLGC198901003.htm [14] 王仁智. 表面喷丸强化机制[J]. 机械工程材料, 1988(5): 21-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC198805006.htmWANG R Z. On the strengthening mechanism of shot peening[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 1988(5): 21-25. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC198805006.htm [15] TSUJI N, TANAKA S, TAKASUGI T. Effects of combined plasma-carburizing and shot-peening on fatigue and wear properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2009, 203(10-11): 1400-1405. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2008.11.013 [16] ZHOU L C, PAN X L, SHI X S, et al. Research on surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with compound treatment of laser shock peening and shot peening[J]. Vacuum, 2022, 196: 110717. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110717 [17] 李世平, 刘道新, 李瑞鸿, 等. 喷丸强化与表面完整性对TC21钛合金疲劳性能的影响[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2012, 31(12): 1921-1926. https://journals.nwpu.edu.cn/jxkxyjs/article/id/5443LI S P, LIU D X, LI R H, et al. Influence of shot peening and surface integrity on fatigue properties of TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2012, 31(12): 1921-1926. (in Chinese) https://journals.nwpu.edu.cn/jxkxyjs/article/id/5443 [18] XU Z K, DUNLEAVEY J, ANTAR M, et al. The influence of shot peening on the fatigue response of Ti-6Al-4V surfaces subject to different machining processes[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2018, 111: 196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.02.022 [19] YANG Q, ZHOU W L, ZHONG Y N, et al. Effect of shot-peening on the fretting wear and crack initiation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V dovetail joint specimens[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2018, 107: 83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.10.020 [20] 高玉魁. 不同表面改性强化处理对TC4钛合金表面完整性及疲劳性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(8): 915-922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201608003.htmGAO Y K. Influence of different surface modification treatments on surface integrity and fatigue performance of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(8): 915-922. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201608003.htm [21] YAO C F, WU D X, MA L F, et al. Surface integrity evolution and fatigue evaluation after milling mode, shot-peening and polishing mode for TB6 titanium alloy[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 387: 1257-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.06.162 [22] 田硕, 杨斌涛, 盖鹏涛, 等. 整体叶盘叶片喷丸强化变形数值模拟及试验研究[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37 (sup.2): 479-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB2023S2076.htmTIAN S, YANG B T, GAI P T, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental research on shot peening deformation of blisk blade[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(sup.2): 479-484. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB2023S2076.htm -







 下载:
下载: