Study on Thermal Characteristics in Hydrogen Absorption of LaNi5 Hydrogen Storage Alloy
-
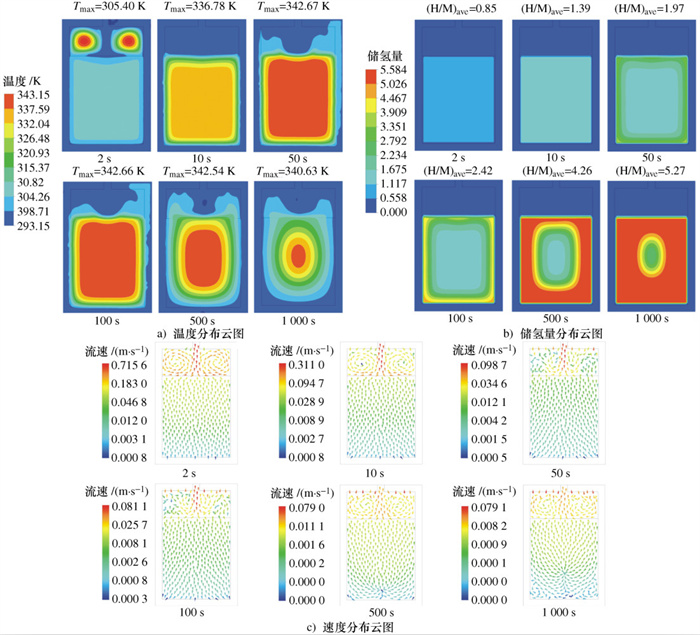
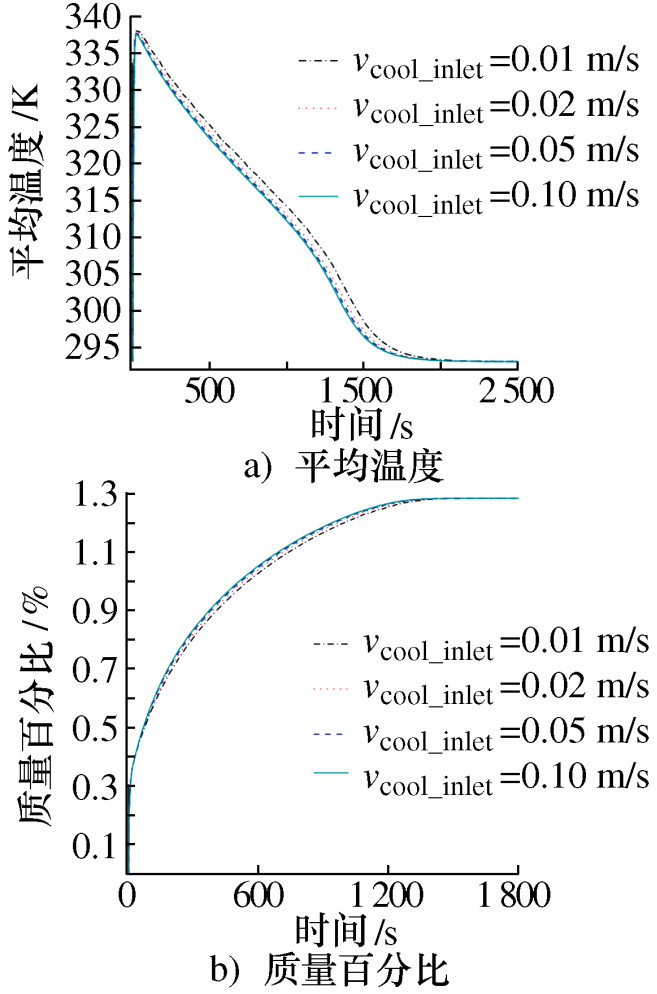
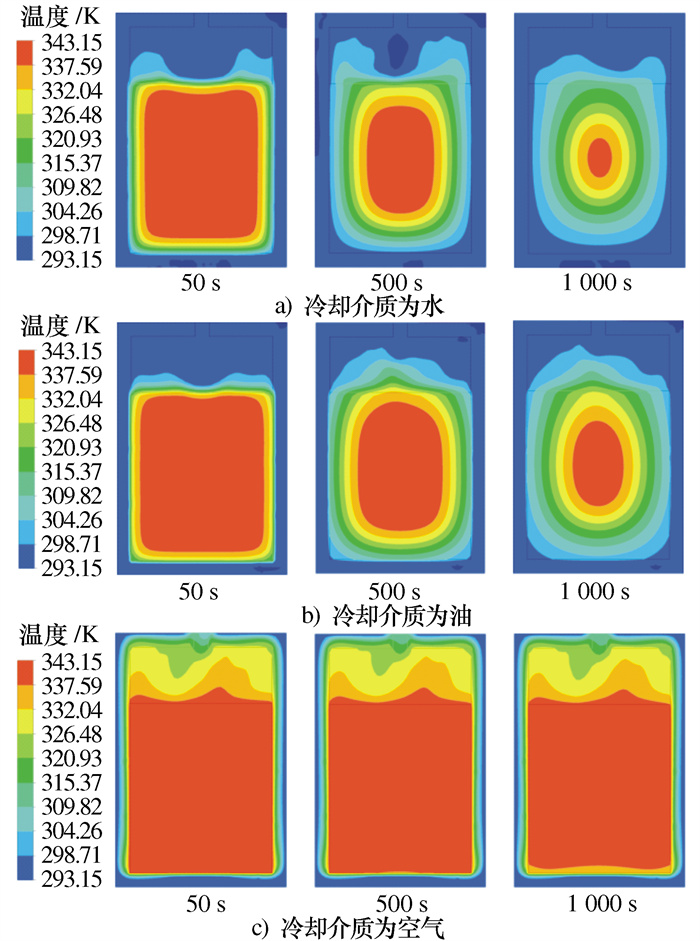
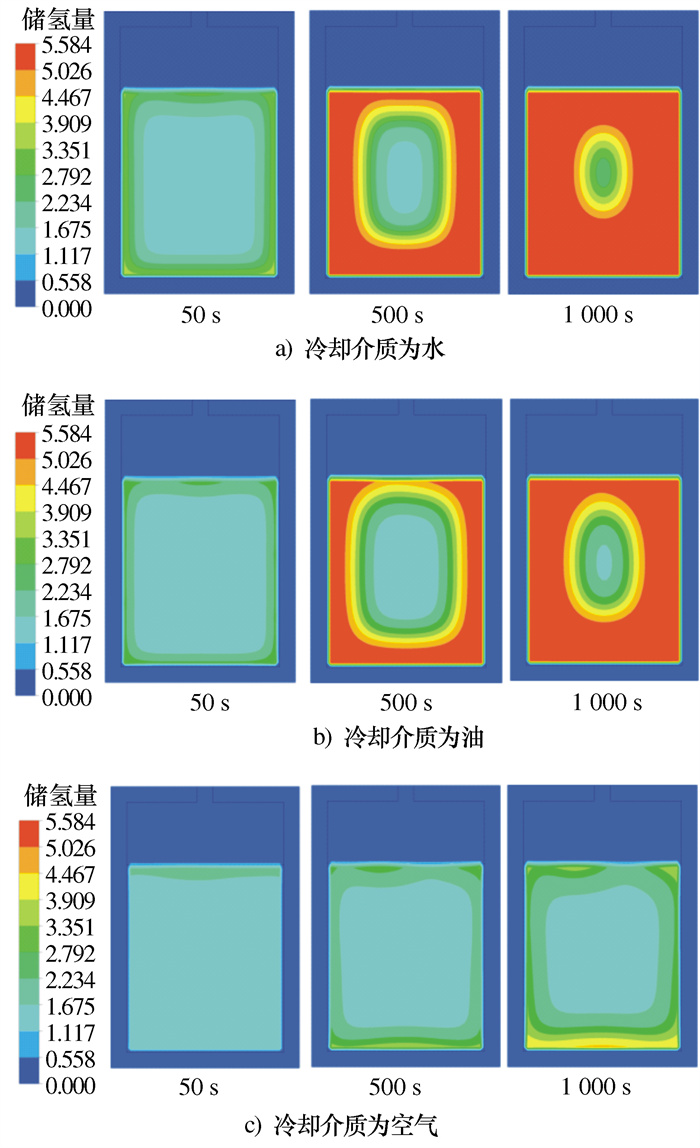
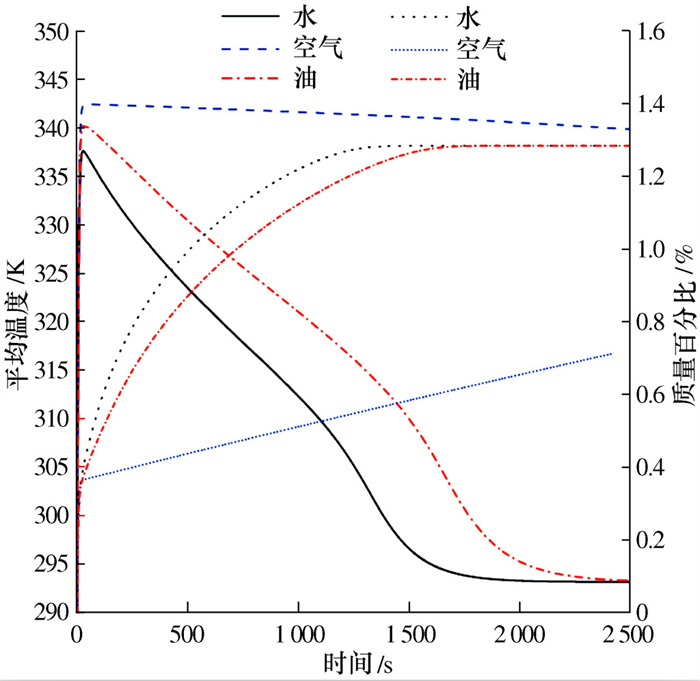
摘要: 建立了某金属氢化物反应器二维数值模型,并通过吸氢实验中反应器温度变化曲线验证了模型的准确性。对储氢反应器增加外部冷却槽,分析了不同冷却流体种类及流速下,反应器温度和储氢量的变化情况。结果表明:冷却水作用下,储氢罐中心区域的反应速率逐渐低于壁面区域,冷却水流速率越高,吸氢反应所需时间逐渐缩短至一个定值; 在相同流速下,冷却介质为水和油时,反应器温度与储氢量的变化特征相似,但水的冷却时间比油缩短约20%、储氢时间缩短约15%;当冷却介质为空气时,冷却槽内空气受热浮力影响,靠近壁面的空气流速降低且温度高于初始值,导致其与合金的温差缩小、传热能力降低,吸氢时间明显加长。Abstract: A two-dimensional numerical simulation model for a metal hydride hydrogen storage tank was established, and the accuracy of the model was verified by using the temperature curve of the tank from experiment. An external cooling channel was added to the tank, the temperature and hydrogen storage amount of the model were analyzed under the different type and flow rate of cooling fluid. The results show that the reaction rate in the center area of the tank is lower than that in wall area under the action of cooling water. With the increasing of cooling water flow rate, the total time of reaction is reduced to a fixed value. At the same flow rate, the variation tendency for water and oil is similar. However, the cooling time and the hydrogen storage time of water are shorter nearly 20% and 15%, respectively. Because of the buoyancy effect, the air velocity closed to the wall decreases and higher than initial temperature, so that the temperature difference between the air and alloy is reduced, the heat transfer capacity is reduced, and the hydrogen absorption time is obviously prolonged.
-
表 1 主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters
参数 数值 初始温度T0/℃ 20 参考温度Tref/℃ 30 入口压强Pin/bar 10 参考压强Pref/bar 10 吸氢速率常数Ca/s 59.187 活化能Ea/(J•mol-1) 21 179.6 氢气热容CpH/[J•(mol•K)-1] 1 489 储氢合金热容CpM/[J•(mol•K)-1] 419 氢气导热系数kg/[W•(m•K)-1] 0.167 合金导热系数ks/[W•(m•K)-1] 3.18 储氢合金孔隙率ε 0.63 孔隙区渗透率K/m2 10-8 冷却温度Ts/℃ 20 合金密度ρM/(kg•m-3) 5 300 饱和合金密ρsat/(kg•m-3) 5 369 表 2 冷却介质的属性参数
Table 2. Attribute properties
冷却介质 水 油 空气 热容/[J•(mol•K)-1] 4 182 1 845 1 006.43 导热系数/[W•(m•K)-1] 0.6 0.145 0.024 2 -
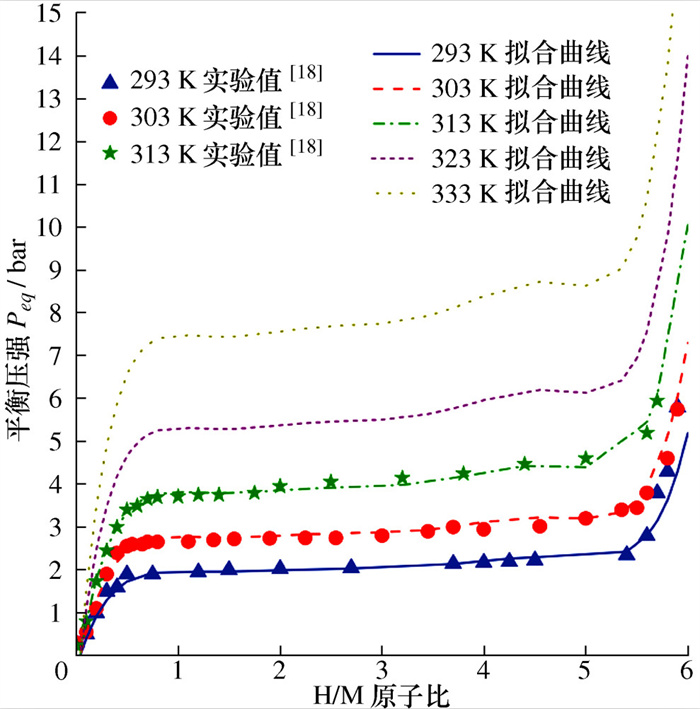
[1] THOMAS K M. Hydrogen adsorption and storage on porous materials[J]. Catalysis Today, 2007, 120(3-4): 389-398. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2006.09.015 [2] RUSMAN N A A, DAHARI M. A review on the current progress of metal hydrides material for solid-state hydrogen storage applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(28): 12108-12126. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.244 [3] BARTHELEMY H, WEBER M, BARBIER F. Hydrogen storage: recent improvements and industrial perspectives[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(11): 7254-7262. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.178 [4] SONG J, WANG Y Q, LI S S, et al. Numerical and experimental study of La-Ni hydriding kinetics based on the varying-size model[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 176: 580-599. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.11.010 [5] 鲍泽威, 朱泽志, 牟晓锋, 等. 金属氢化物储氢反应器放氢特性的数值模拟[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2021, 53(2): 151-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH202102018.htmBAO Z W, ZHU Z Z, MOU X F, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrogen desorption characteristics in metal hydride reactor for hydrogen storage[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2021, 53(2): 151-157. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH202102018.htm [6] BAYKARA S Z. Hydrogen: a brief overview on its sources, production and environmental impact[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(23): 10605-10614. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.022 [7] MARTY P, DE RANGO P, DELHOMME B, et al. Various tools for optimizing large scale magnesium hydride storage[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 580(S1): S324-S328. [8] NAM J, KO J, JU H. Three-dimensional modeling and simulation of hydrogen absorption in metal hydride hydrogen storage vessels[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 89(1): 164-175. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.06.015 [9] CHIPPAR P, LEWIS S D, RAI S, et al. Numerical investigation of hydrogen absorption in a stackable metal hydride reactor utilizing compartmentalization[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(16): 8007-8017. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.017 [10] CHANDRA S, SHARMA P, MUTHUKUMAR P, et al. Modeling and numerical simulation of a 5kg LaNi5-based hydrogen storage reactor with internal conical fins[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(15): 8794-8809. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.01.115 [11] EL MGHARI H, HUOT J, XIAO J S. Analysis of hydrogen storage performance of metal hydride reactor with phase change materials[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(54): 28893-28908. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.090 [12] WANG Y, ADROHER X C, CHEN J X, et al. Three-dimensional modeling of hydrogen sorption in metal hydride hydrogen storage beds[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 194(2): 997-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.06.060 [13] KYOUNG S, FEREKH S, GWAK G, et al. Three- dimensional modeling and simulation of hydrogen desorption in metal hydride hydrogen storage vessels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(41): 14322-14330. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.03.114 [14] CHIBANI A, BOUGRIOU C. Effect of the tank geometry on the storage and destocking of hydrogen on metal hydride (LaNi5-H2)[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(36): 23035-23044. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.07.102 [15] JEMNI A, NASRALLAH S B, LAMLOUMI J. Experimental and theoretical study of Ametal-hydrogen reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 1999, 24(7): 631-644. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(98)00117-7 [16] GKANAS E I, GRANT D M, KHZOUZ M, et al. Efficient hydrogen storage in up-scale metal hydride tanks as possible metal hydride compression agents equipped with aluminium extended surfaces[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(25): 10795-10810. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.04.035 [17] ASKRI F, JEMNI A, NASRALLAH S B. Dynamic behavior of metal-hydrogen reactor during hydriding process[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2004, 29(6): 635-647. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3199(03)00220-9 [18] DHAOU H, ASKRI F, SALAH M B, et al. Measurement and modelling of kinetics of hydrogen sorption by LaNi5 and two related pseudobinary compounds[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(5): 576-587. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2006.07.001 -







 下载:
下载: