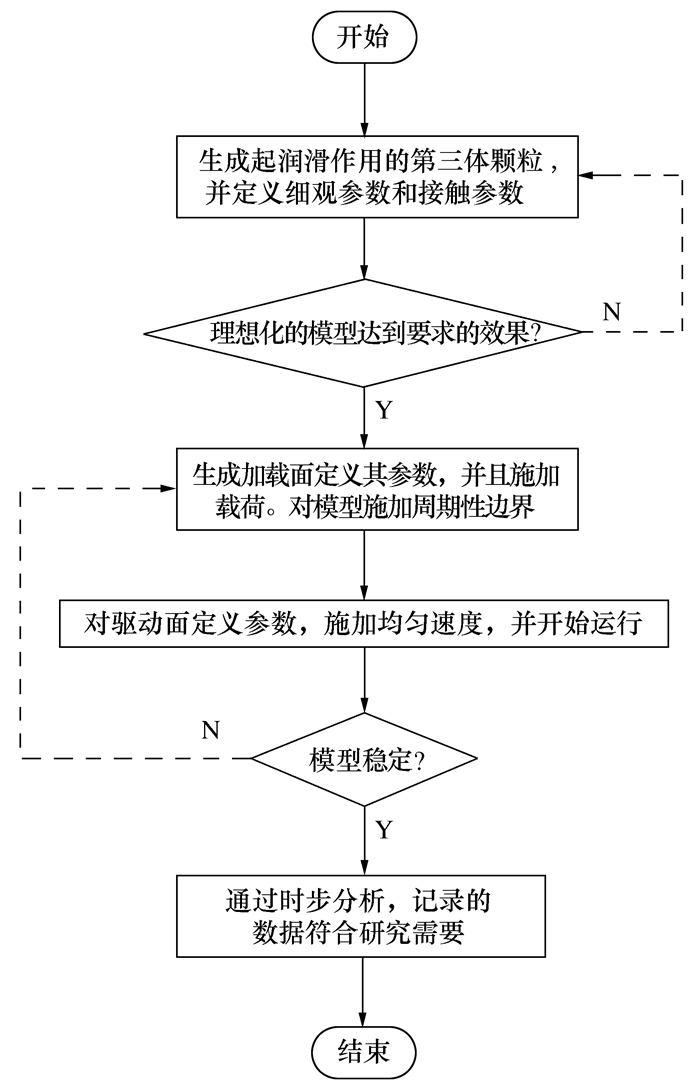
Mechanical Mechanisms of Shear Dilatancy and Force Chain Evolution in Abrasive Polishing Granular Flow
-
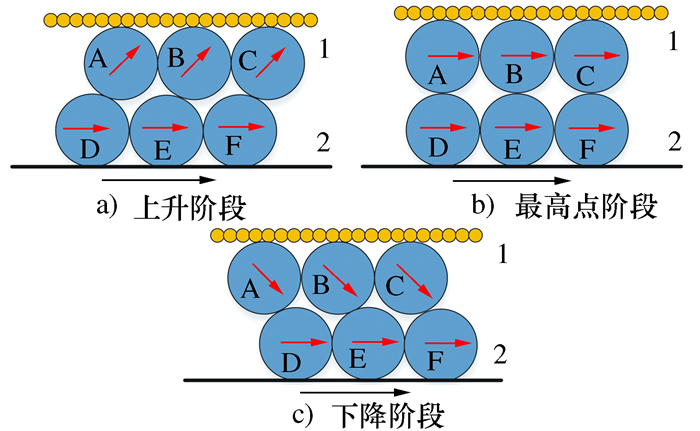
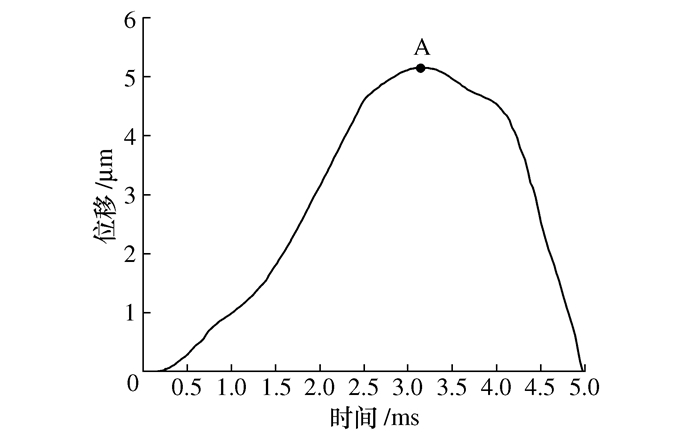
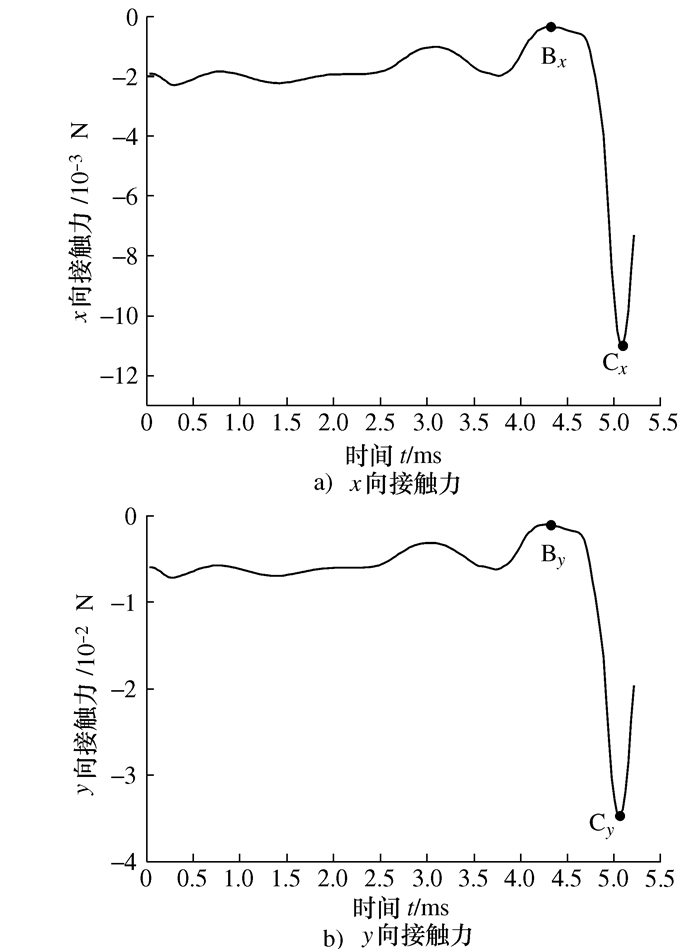
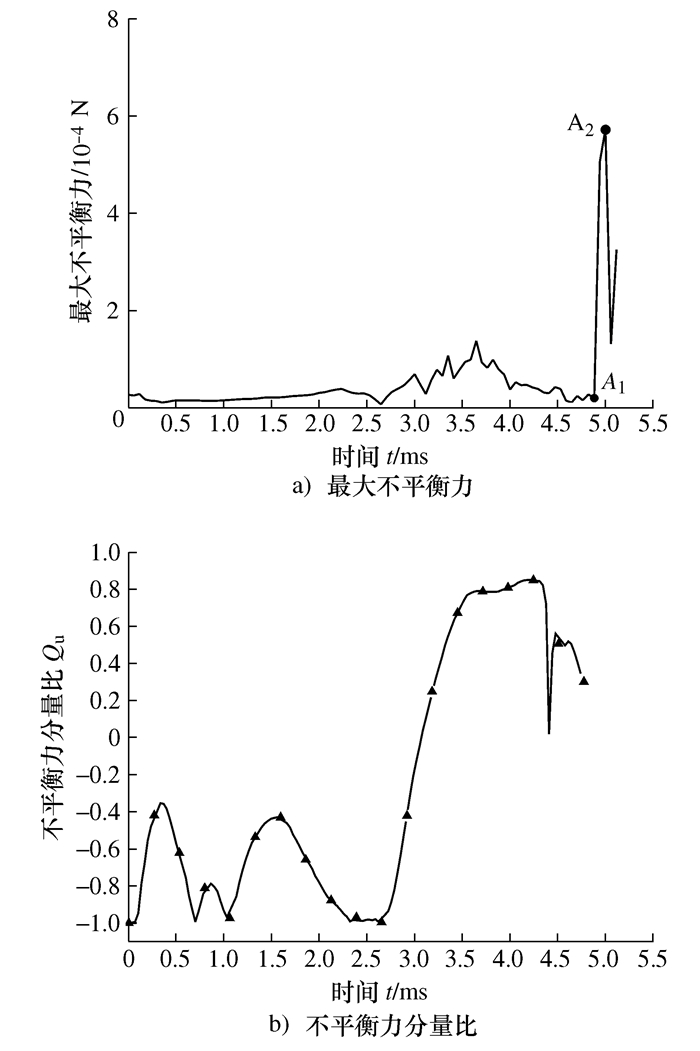
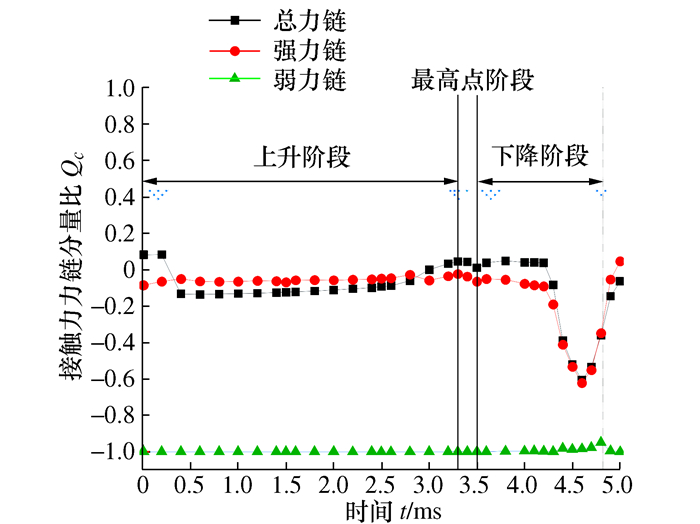
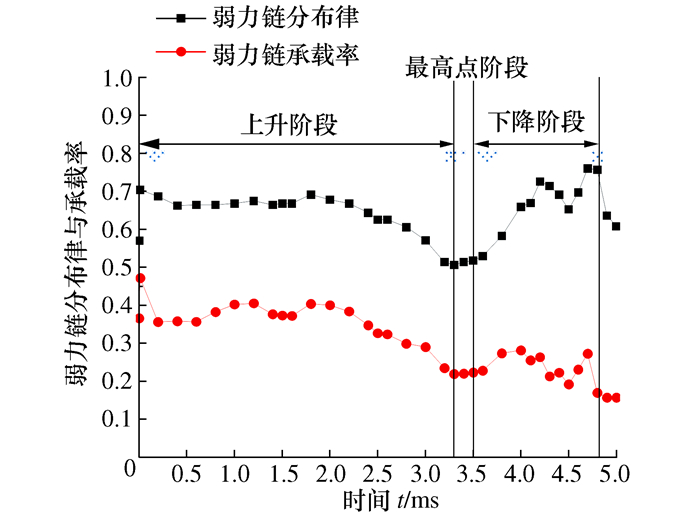
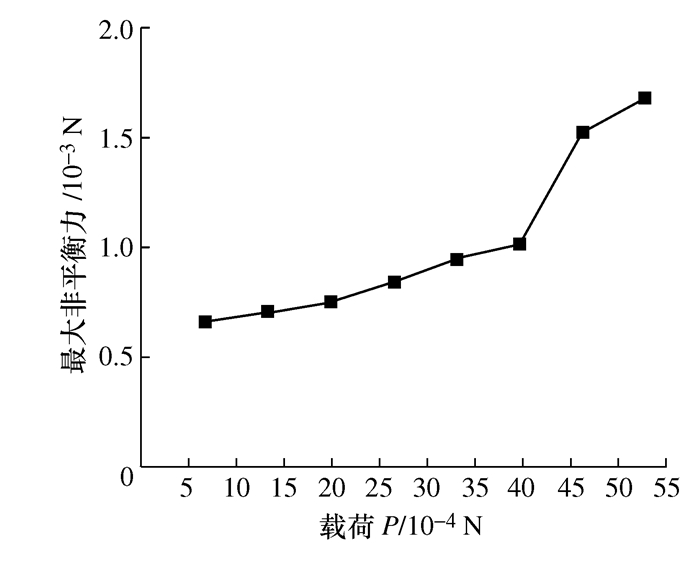
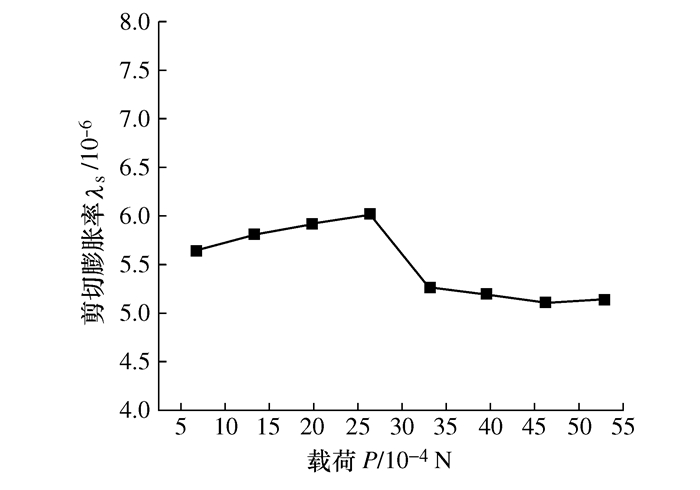
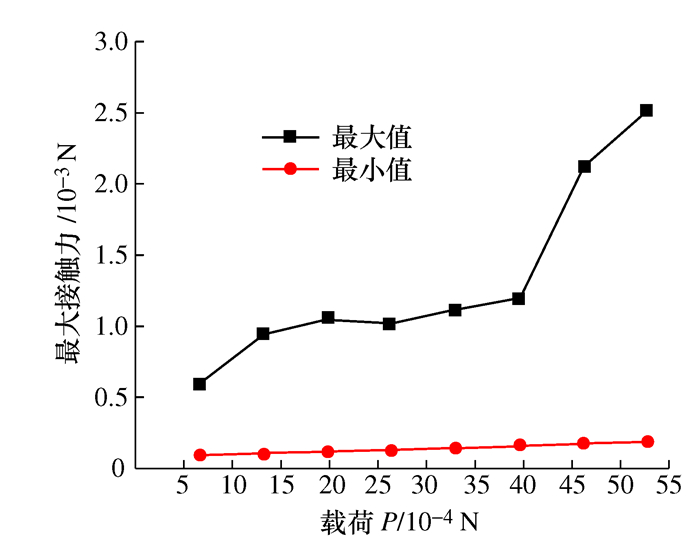
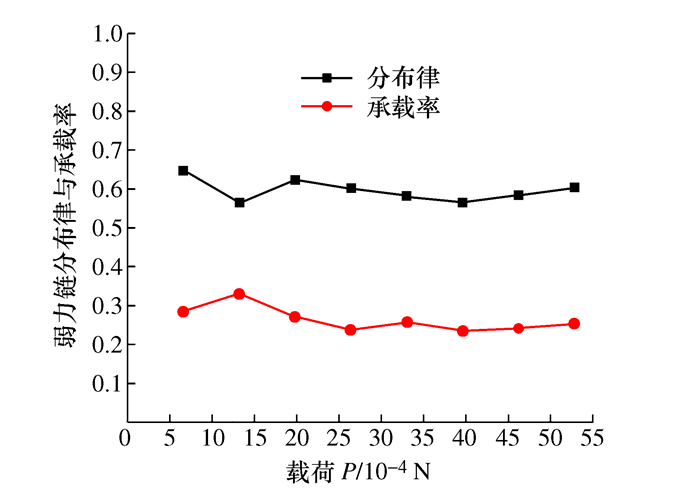
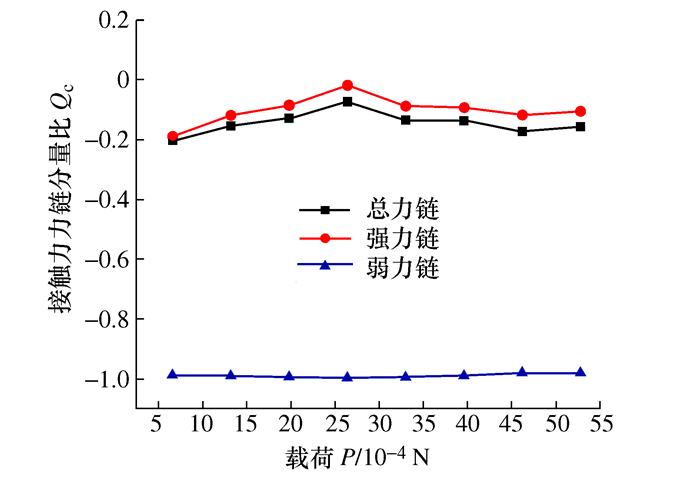
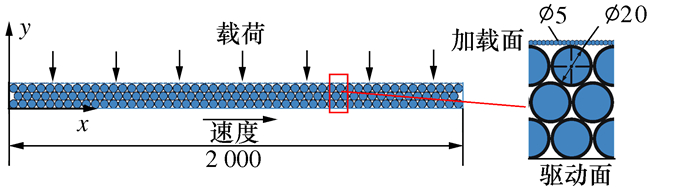
摘要: 将研磨抛光作为后处理可以提高工件的表面质量, 如何将研磨抛光工艺价值最大化是本文首要解决的问题。由于颗粒流润滑既适用于极端环境又具有环保作用, 因此本文将颗粒流用于研磨抛光。通过离散单元法建立平行板结构模型, 将颗粒流作为第三体填充至摩擦副间隙, 将工件表面与刀具作为第一体对颗粒流体系施加法向力和剪切力, 对研磨抛光过程进行数值模拟。研究结果表明: 单个颗粒剪切膨胀过程可以分为上升阶段、最高点阶段和下降阶段, 不同阶段的弱力链方向都偏向于x轴, 其中上升阶段强弱力链方向稳定, 可提高工件的加工效率以及表面质量。当载荷的较大, 会使强弱力链的分布律与承载率稳定, 当载荷较大及较小时, 剪切膨胀率降低, 强力链方向更偏向于x轴。通过本研究, 可以将不易检测的力链和剪切膨胀现象进行数值模拟, 为研磨抛光条件下使用颗粒流提供了理论基础。Abstract: The use of grinding and polishing as post processing can improve the surface quality of a workpiece. This paper mainly solves the problem of how to maximize the values of grinding and polishing processes. Since granular flow lubrication is suitable for extreme environment and environmental protection, the paper uses granular flow for grinding and polishing. A parallel plate model was established with the discrete element method. Granular flow was used as the third body to fill the gap between friction pairs, and the workpiece surface and tool were used as the first body to apply normal force and shear force to the granular flow system. The polishing process was numerically simulated. The results show that the shear dilatancy process of a single particle can be divided into rising stage, peak stage and falling stage. The weak chain direction in different stages is inclined to the x axis. In the rising stage, the weak chain direction is stable and can improve the machining efficiency and surface quality of the workpiece. When the load is large, the distribution law and the bearing rate of strong and weak force chains are stable. When the load is small, the shear dilatancy rate decreases and the strong chain direction is inclined to the x axis. This study numerically simulates the force chain and shear dilatancy that are not easily detected, thus providing a theoretical basis for the use of granular flow under the condition of grinding and polishing.
-
Key words:
- grinding and polishing /
- granular flow /
- discrete element method /
- force chain /
- shear dilatancy
-
表 1 参数名称及数值
Table 1. The names and values of parameters
参数 数值 上部加载面载荷P/10-4 N 6.60 加载面密度/(kg·m-3) 8 190 加载面剪切模量/GPa 77.20 加载面泊松比 0.30 加载面与颗粒的摩擦因数 0.36 颗粒的粒径D/μm 40 颗粒间摩擦因数 0.24 下部驱动面速度v/(m·s-1) 0.50 驱动面与颗粒间摩擦因数 0.32 颗粒密度/(kg·m-3) 2 400 颗粒的剪切模量/GPa 198 颗粒的泊松比 0.17 颗粒的层数L 3 -
[1] 张宏君. 研磨、珩磨、抛光技术在机械制造中的应用[J]. 黑龙江科学, 2021, 12(8): 108-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8646.2021.08.047ZHANG H J. Application of grind, honing and polishing technology in machine manufacturing[J]. Heilongjiang Science, 2021, 12(8): 108-109. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8646.2021.08.047 [2] 周光明. 铁素体不锈钢研磨工艺研发与应用[J]. 山西冶金, 2021, 44(4): 50-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYZ202104017.htmZHOU G M. Development and application of ferrite stainless steel grinding process[J]. Shanxi Metallurgy, 2021, 44(4): 50-52. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYZ202104017.htm [3] JIAO Z H, KANG R K, DONG Z G, et al. Microstructure characterization of W-Ni-Fe heavy alloys with optimized metallographic preparation method[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2019, 80: 114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.01.011 [4] 罗桂海. 新型石材研磨抛光技术与基体特性研究[J]. 现代制造技术与装备, 2019(6): 13-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5587.2019.06.009LUO G H. Study on the characteristics of new stone grinding and polishing[J]. Modern Manufacturing Technology and Equipment, 2019(6): 13-14. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5587.2019.06.009 [5] 史晓琳. 钨合金研磨抛光表面形貌形成机理及工艺研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020.SHI X L. Study on surface topography formation mechanism and process in lapping and polishing of tungsten alloy[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020. (in Chinese) [6] 郑锦华, 吴双, 魏新煦, 等. 研磨抛光表面微孔织构的形成[J]. 光学精密程, 2016, 24(4): 788-795. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201604014.htmZHENG J H, WU S, WEI X X, et al. Formation of surface micro-pore texture by grinding and polishing[J]. Optical and Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(4): 788-795. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201604014.htm [7] 刘宁, 朱永伟, 李学, 等. 硬脆材料平面研抛的材料去除机理研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(7): 21060121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB202207007.htmLIU N, ZHU Y W, LI X, et al. Research progress of material removal mechanism in plane lapping and polishing of hard-brittle materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(7): 21060121. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB202207007.htm [8] KILIÇ V, GÖK A. Effect of different polishing systems on the surface roughness of various bulk-fill and Nano-filled resin-based composites: An atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy study[J]. Microscopy Research and Technique, 2021, 84(9): 2058-2067. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23761 [9] DE SOUZA R H, KAIZER M R, BORGES C E P, et al. Flexural strength and crystalline stability of a monolithic translucent zirconia subjected to grinding, polishing and thermal challenges[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(16): 26168-26175. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.114 [10] LI J, TANG Y K, SONG L L, et al. Effect of FAP characteristics on fixed abrasive polishing of CaF2crystal[J]. International Journal of Nanomanufacturing, 2019, 15(3): 259-268. doi: 10.1504/IJNM.2019.100460 [11] CADORE-RODRIGUES A C, MACHRY R V, ZUCUNI C P, et al. Grinding and polishing of the inner surface of monolithic simplified restorations made of zirconia polycrystals and lithium disilicate glass-ceramic: Effects on the load-bearing capacity under fatigue of the bonded restorations[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2021, 124: 104833. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104833 [12] ZUCUNI C P, PEREIRA G K R, VALANDRO L F. Grinding, polishing and glazing of the occlusal surface do not affect the load-bearing capacity under fatigue and survival rates of bonded monolithic fully-stabilized zirconia simplified restorations[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2020, 103: 103528. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2019.103528 [13] 张桐齐, 岳晓斌, 雷大江, 等. 磨粒半径对金刚石研磨加工影响机制的仿真研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2021, 41(1): 89-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGSM202101016.htmZHANG T Q, YUE X B, LEI D J, et al. Simulation study on influence mechanism of abrasive radius on diamond grinding[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 89-94. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGSM202101016.htm [14] 李俊烨, 胡敬磊, 杨兆军, 等. 离散相磨粒粒径对磨粒流研抛共轨管质量的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 492-499. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201802020.htmLI J Y, HU J L, YANG Z J, et al. Effect of the size of discrete phase abrasive particles on the abrasive flow polishing quality of common rail pipe[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(2): 492-499. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201802020.htm [15] XIAO X L, LI G X, MEI H J, et al. Polishing of silicon nitride ceramic balls by clustered magnetorheological finish[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(3): 304. doi: 10.3390/mi11030304 [16] 赵金鑫. 基于离散元法的卧式行星研磨机筒内介质仿真分析[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学, 2021.ZHAO J X. Simulation analysis of the medium in the cylinder of the horizontal planetary Grinder Based on the discrete element method[D]. Anshan: University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021. (in Chinese) [17] 李奎. 磁粒研磨加工过程的离散元仿真分析[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学, 2021.LI K. Discrete element simulation analysis of magnetic abrasive finishing[D]. Anshan: University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021. (in Chinese) [18] XIU T X, WANG W, LIU K, et al. Characteristics of force chains in frictional interface during abrasive flow machining based on discrete element method[J]. Advances in Manufacturing, 2018, 6(4): 355-375. doi: 10.1007/s40436-018-0236-7 [19] 石崇, 张强, 王盛年. 颗粒流(PFC5.0)数值模拟技术及应用[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018: 87-88.SHI C, ZHANG Q, WANG S N. Numerical simulation technology and application with particle flow code (PFC5.0)[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018: 87-88. (in Chinese) [20] IORDANOFF I, KHONSARI M M. Granular lubrication: toward an understanding of the transition between kinetic and quasi-fluid regime[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2004, 126(1): 137-145. doi: 10.1115/1.1633575 [21] CUNDALL P A, STRACK A. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Geotechnique, 1979, 29(1): 47-65. doi: 10.1680/geot.1979.29.1.47 [22] 石崇, 徐卫亚. 颗粒流数值模拟技巧与实践[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015: 1-2.SHI C, XU W Y. Numerical simulation skills and practice of particle flow[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015: 1-2. (in Chinese) [23] 江凯. 聚合物复合材料摩擦界面纵向迁移的数值模拟[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016.JIANG K. Numerical simulation of the vertical migration on the friction interface of polymeric composites[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese) -







 下载:
下载: