Application of Improved MobileNet Network in Bearing Lightweight Diagnosis
-
摘要: 近年来,基于神经网络的故障诊断方法在诊断的准确性、效率等方面展现出巨大的优势,然而呈指数增长的模型参数量限制了神经网络在工程实际中的应用。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种基于一维卷积神经网络改进的MobileNet网络用于实现滚动轴承的故障诊断;改进的网络能够直接应用于一维振动信号,有效降低系统硬件资源的要求,实现网络的轻量化部署;使用西储大学轴承数据集和QPZZ-Ⅱ型故障模拟试验台数据集对所提方法进行验证,本文提出的模型准确率均达99.8%以上,参数量为标准卷积神经网络的1/2。本文所提方法为在轻资源嵌入式系统中实现智能诊断提供了一种新的方法和思路。Abstract: In recent years, fault diagnosis methods based on neural networks have shown great advantages in the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis. However, the exponentially increasing number of model parameters limits the application of neural networks in engineering practice. Aiming at this problem, this paper proposes an improved MobileNet network based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network for fault diagnosis of rolling bearings. The improved network can be directly applied to one-dimensional vibration signals, effectively reducing the requirements of system hardware resources and realizing lightweight deployment of the network; The proposed method is validated using the Western Reserve University bearing dataset and the QPZZ-Ⅱ fault simulation test bench dataset. The accuracy of the model proposed in this paper is more than 99.8%, and the number of parameters is 1/2 of the standard convolutional neural network. The method proposed provides a new way for realizing intelligent diagnosis in light-resource embedded systems.
-
Key words:
- rolling bearing /
- fault diagnosis /
- neural network /
- MobileNet
-
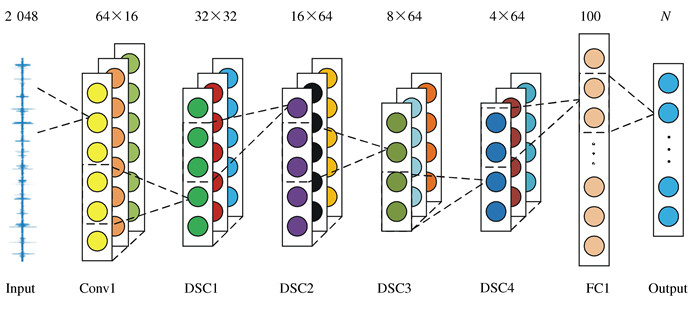
表 1 1D-CNN网络参数设置
Table 1. 1D-CNN network parameters
No. Layers Kernel size/pool size Activation Input size Output size 1 Conv1 64×1×16 ReLu 6.0 2 048×1 128×16 2 Maxpooling1 2×1 128×16 64×16 3 DSC1 6×1×32 ReLu 6.0 64×16 64×32 4 Maxpooling2 2×1 64×32 32×32 5 DSC2 6×1×64 ReLu 6.0 32×32 32×64 6 Maxpooling3 2×1 32×64 16×64 7 DSC3 6×1×64 ReLu 6.0 16×64 16×64 8 Maxpooling4 2×1 16×64 8×64 9 DSC4 6×1×64 ReLu 6.0 8×64 8×64 10 Maxpooling5 2×1 8×64 4×64 11 Flatten 4×64 256×1 12 FC1 100×1 ReLu 256×1 100×1 13 FC2 N×1 Softmax 100×1 N×1 表 2 实验1数据集
Table 2. Experiment 1 data set
实验对象 负载 样本数 样本长度 故障类型 故障直径/mm 标签 6205-2RS JEM SKF 1.5 kW 1 000 2 048 正常 0 0 1 000 2 048 滚动体 0.007 1 1 000 2 048 滚动体 0.014 2 1 000 2 048 滚动体 0.021 3 1 000 2 048 内圈 0.007 4 1 000 2 048 内圈 0.014 5 1 000 2 048 内圈 0.021 6 1 000 2 048 外圈 0.007 7 1 000 2 048 外圈 0.014 8 1 000 2 048 外圈 0.021 9 表 3 不同模型性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of different models
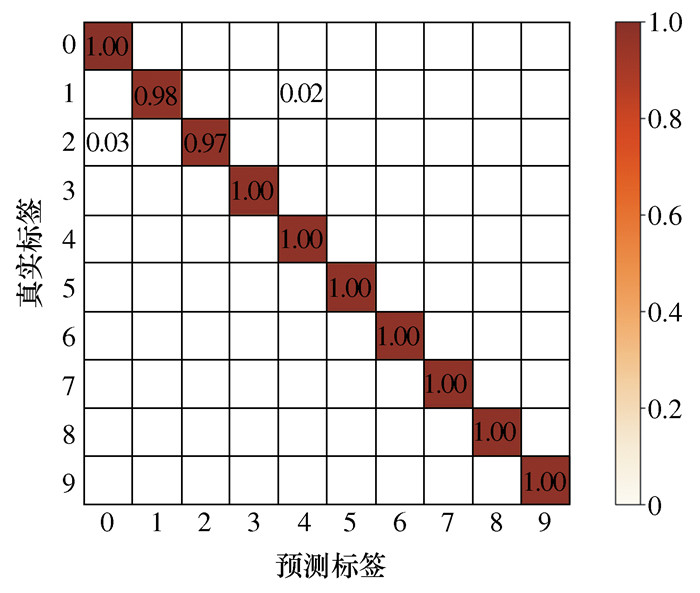
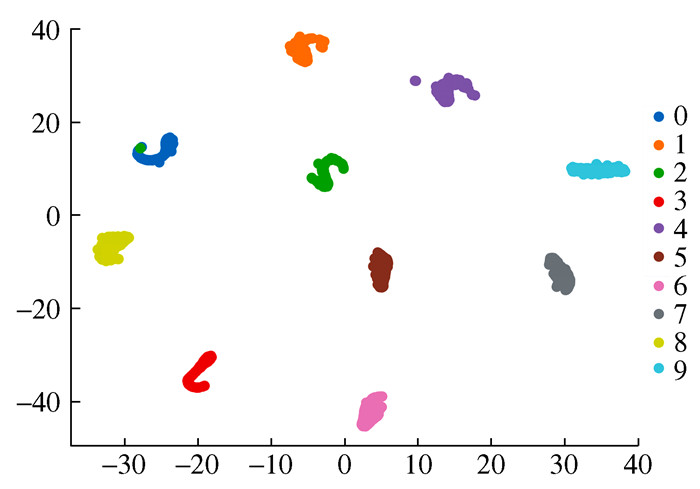
模型 准确率/% 模型参数量 预测时间/s 1D-CNN 99.6 30 998 2.495 9 标准CNN 99.9 61 190 3.961 8 SVM 88 表 4 实验2数据表
Table 4. Experiment 2 data set
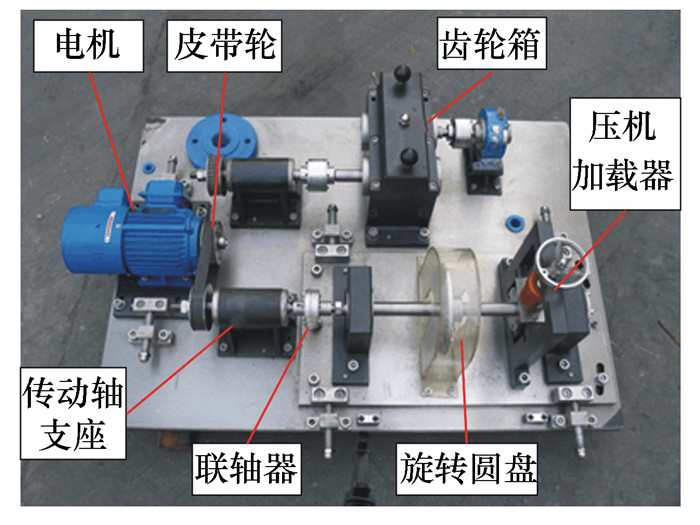
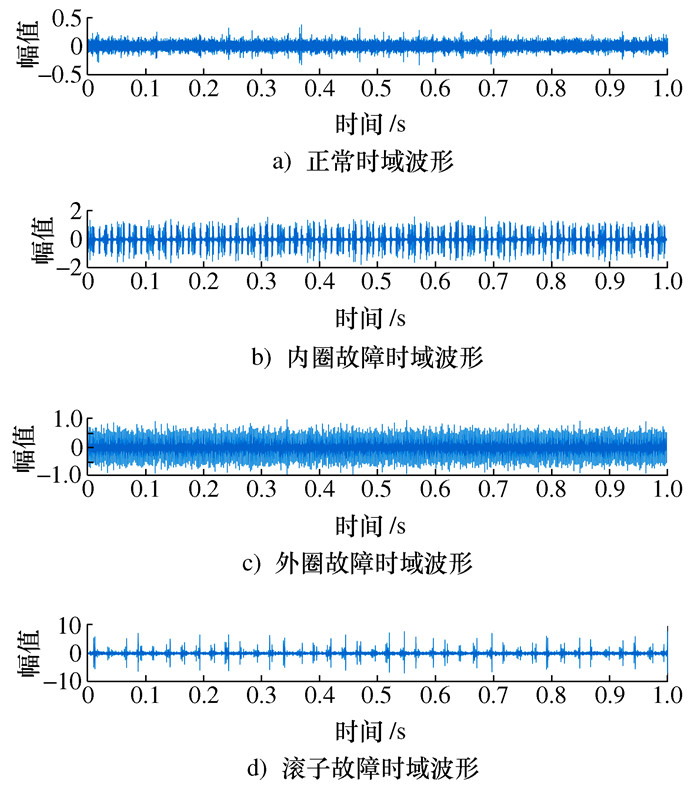
实验对象 负载 转速/(r·min-1) 样本数量 样本长度 状态 标签 圆柱滚子轴承N205EN 30 kg 1 200 1 000 2 048 正常 0 1 200 1 000 2 048 内圈故障 1 1 200 1 000 2 048 外圈故障 2 1 200 1 000 2 048 滚动体故障 3 表 5 模型性能对比
Table 5. Model performance comparison
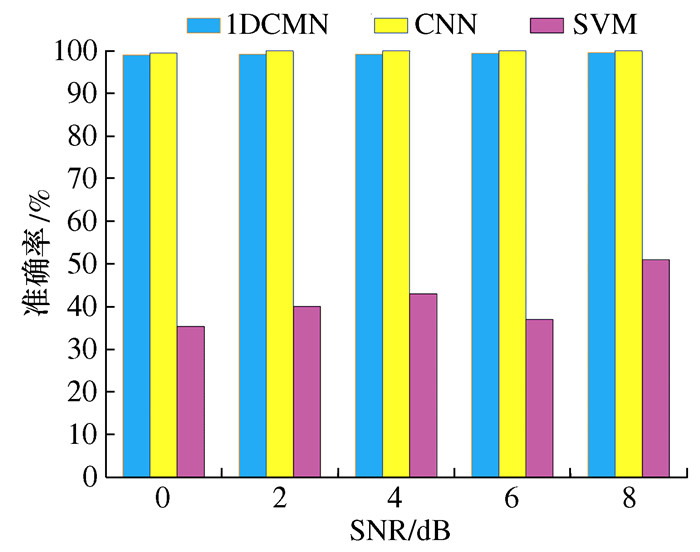
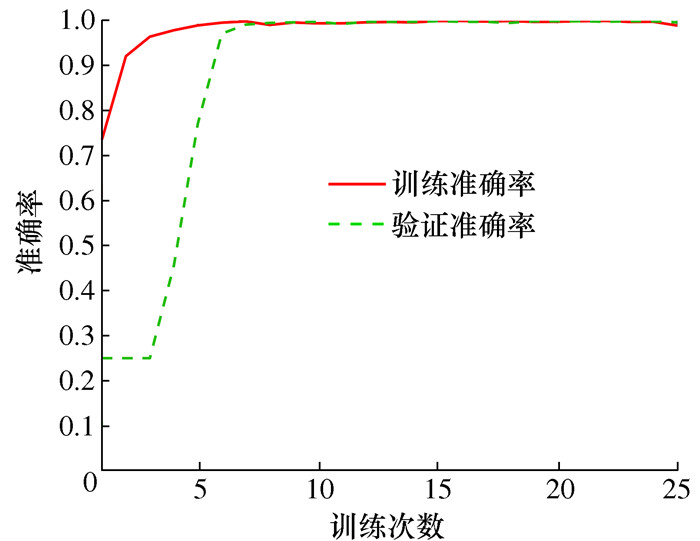
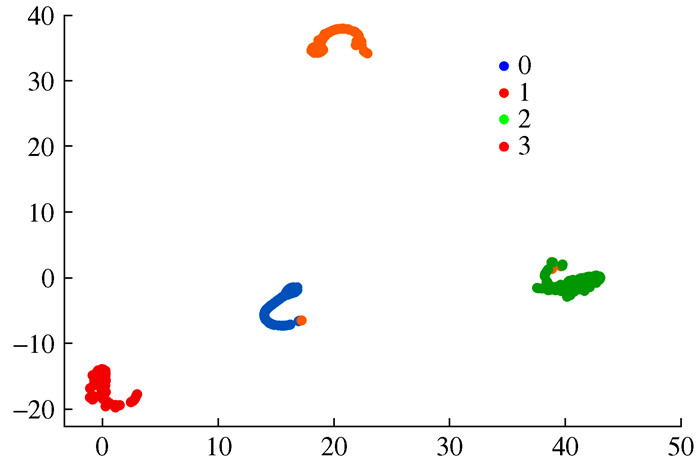
模型 准确率/% 模型参数量 预测时间/s 1D-CNN 100 30 192 2.403 5 标准CNN 100 59 188 3.621 1 SVM 84.375 -
[1] 李道军, 李廷锋, 刘德平. 基于LMD与改进SVM的轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 机械制造, 2021, 59(6): 84-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4998.2021.06.021LI D J, LI T F, LIU D P. Bearing fault diagnosis method based on LMD and improved SVM[J]. Machinery, 2021, 59(6): 84-88. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4998.2021.06.021 [2] CHEN Q Q, DAI S W, DAI H D. A rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on EMD and quantile permutation entropy[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, 2019: 3089417. [3] YUAN X J, WU W B, YE F L, et al. Application of a wavelet transform after signal differentiation in fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2020, 105(S1): 61-66. [4] KHORRAM A, KHALOOEI M, REZGHI M. End-to-end CNN+LSTM deep learning approach for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2021, 51(2): 736-751. doi: 10.1007/s10489-020-01859-1 [5] WANG H, XU J W, YAN R Q, et al. Intelligent bearing fault diagnosis using multi-head attention-based CNN[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 49: 112-118. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.07.005 [6] ZHANG W, PENG G L, LI C H, et al. A new deep learning model for fault diagnosis with good anti-noise and domain adaptation ability on raw vibration signals[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(2): 425. doi: 10.3390/s17020425 [7] YE Z, YU J B. Deep morphological convolutional network for feature learning of vibration signals and its applications to gearbox fault diagnosis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2021, 161: 107984. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.107984 [8] Google LLC. Efficient convolutional neural networks and techniques to reduce associated computational costs: US, 20190347537A1[P]. 2019-11-14. [9] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [10] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C] //3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego: ICLR, 2015. [11] YU W B, LV P. An end-to-end intelligent fault diagnosis application for rolling bearing based on MobileNet[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 41925-41933. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3065195 [12] WANG X, MAO D X, LI X D. Bearing fault diagnosis based on vibro-acoustic data fusion and 1D-CNN network[J]. Measurement, 2021, 173: 108518. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108518 [13] 郑一珍, 牛蔺楷, 熊晓燕, 等. 基于一维卷积神经网络的圆柱滚子轴承保持架故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(19): 230-238.ZHENG Y Z, NIU L K, XIONG X Y, et al. Fault diagnosis of cylindrical roller bearing cage based on 1D convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(19): 230-238. (in Chinese) [14] MAULUD D H, AMEEN S Y, OMAR N, et al. Review on natural language processing based on different techniques[J]. Asian Journal of Research in Computer Science, 2021, 10(1): 1-17. [15] 刘恒畅, 姚德臣, 杨建伟, 等. 基于多分支深度可分离卷积神经网络的滚动轴承故障诊断研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(10): 95-102.LIU H C, YAO D C, YANG J W, et al. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on a multi branch depth separable convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(10): 95-102. (in Chinese) -







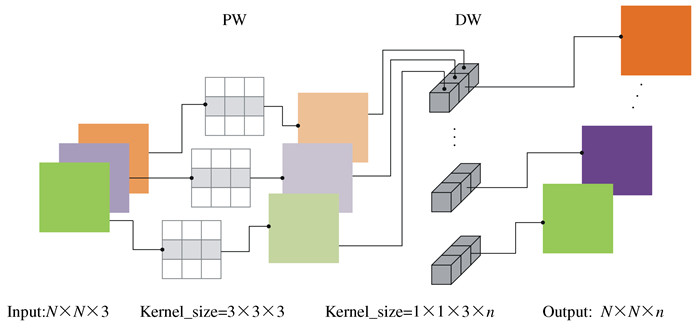
 下载:
下载: