A Coverage Path Planning Method with Reinforcement Learning Considering Manufacturing Process Uncertainty
-
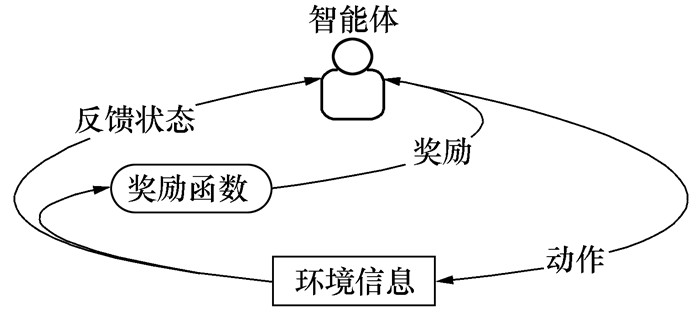
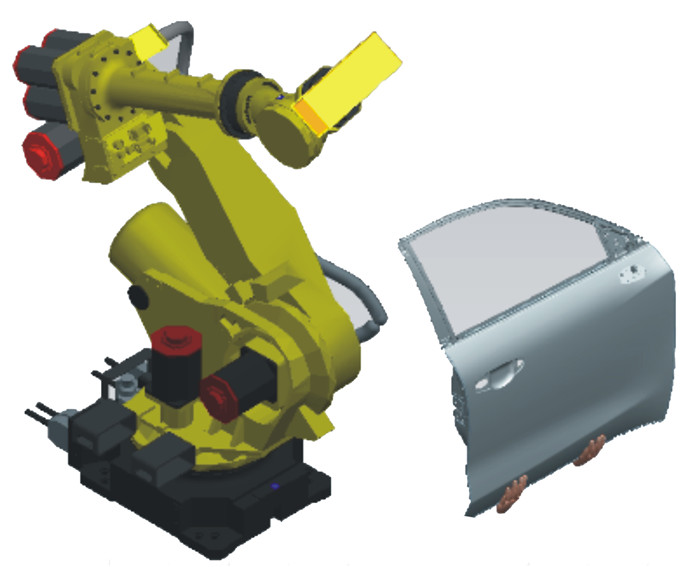
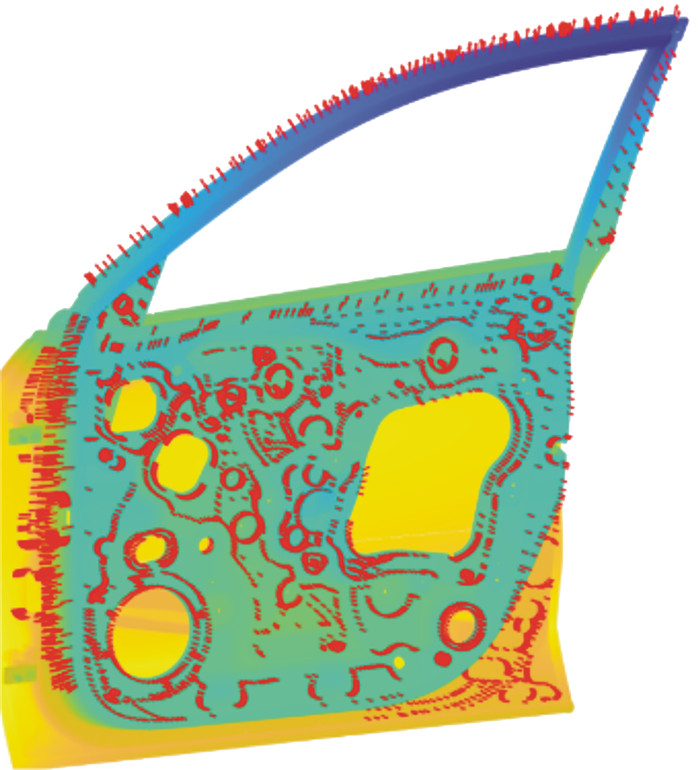
摘要: 机器人扫描测量系统在汽车质量检测领域获得广泛应用,尤其数模环境下基于仿生优化算法的视点采样与路径规划研究取得较大进展。然而,基于名义数模环境的路径规划结果难以适用实际不确定性检测环境。为此,本文提出基于改进的蒙特卡洛树搜索的视点自适应采样方法,在线生成工业机器人运动轨迹。通过车门内板案例的对比分析,验证本文方法的有效性,为实现不确定制造环境下工艺路径的在线规划提供理论依据。Abstract: The robotic scanning system has been widely used in the quality inspection field of automobiles, especially the studies of viewpoint sampling and path planning based on the genetic optimization algorithm in the model-based environment. However, the path planning results based on the nominal models are difficult to apply to the actual inspection environment. To address this problem, a viewpoint adaptive sampling method is proposed based on an improved Monte Carlo tree search, and industrial robot motion trajectories are planned online. Finally, the case of the car door inner panel was used to illustrate the effectiveness of the method.
-
Key words:
- optical inspection /
- coverage path planning /
- manufacturing deviation /
- motion planning
-
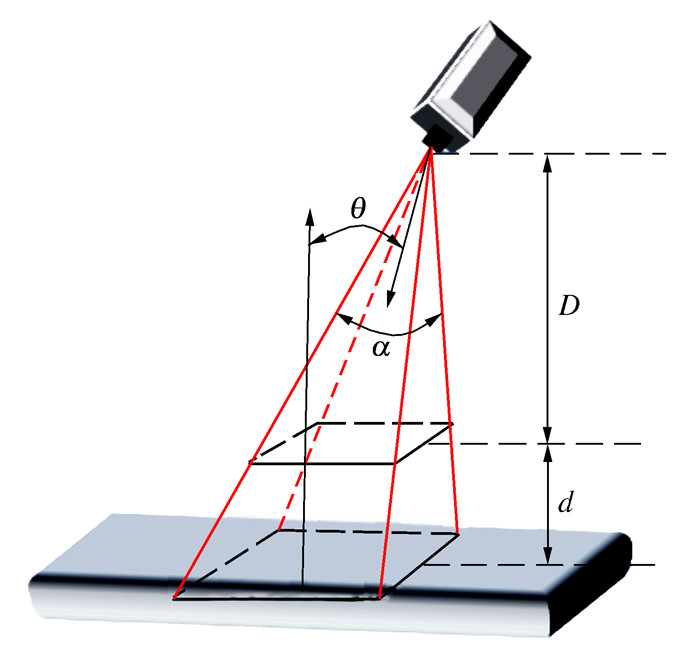
算法1: 蒙特卡洛树搜索(MTCS) 输入: 初始视点位置信息S0 输出: 根据当前节点的状态, 选择最佳子节点S0′ 1: create root node v0 with state S0 2: for i=1: max-iteration: 3: v←TreePolicy(v0) 4: Δ←SimulatePolicy(s(v)) 5: BackUp(v, Δ) 6: end for 7: S0′ ←BestChild(v0) 算法2:树策略(TreePolicy) 输入:当前节点v 输出:当前节点的子节点v′ 1:while v is not terminal: 2:if v is not fully expanded 3:choose v′ from untried s(v) 4:v′ satisfy f(S, a0, a1, …, ai-1) 5:Return (v′) 6:else 7:v′→BestChild(v) 8:Return(v) 算法3:回溯函数(BackUp) 输入:当前节点v,默认策略模拟结果Δ 输出:更新被选择的节点信息 1:while v is not empty: 2:N(v)←N(v)+1 3:Q(v)←Q(v)+Δ 4:v←parent of v 表 1 扫描仪参数
Table 1. Parameters of the scanner
参数 数值 DOF/mm [780, 1 010] FOV 0.330 6 可视角/(°) 60 近端视场 374×374 远端视场 500×500 表 2 基于两种方法的机器人运动时间对比
Table 2. Comparison result Inspection time for full coverage based on two methods
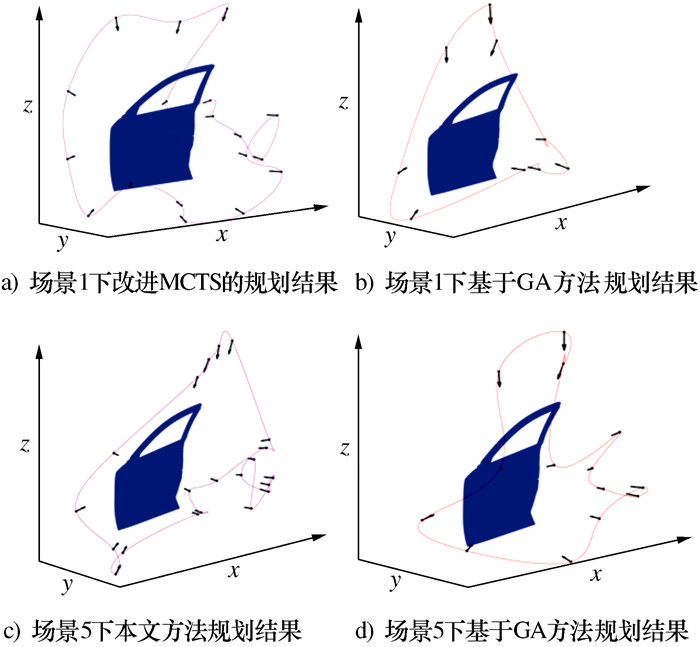
s 场景 方法 实验值 平均值 1 2 3 4 5 1 本文方法 20.57 19.81 20.03 20.60 21.12 20.43 GA 21.27 21.27 21.27 21.27 21.27 21.27 2 本文方法 20.36 20.52 20.32 20.91 20.65 20.55 GA 21.29 21.29 21.29 21.29 21.29 21.29 3 本文方法 21.80 20.27 22.70 21.47 22.43 21.73 GA 22.87 22.87 22.87 22.87 22.87 22.87 4 本文方法 19.29 21.60 20.18 19.67 19.09 19.97 GA 22.39 22.39 22.39 22.39 22.39 22.39 5 本文方法 21.80 21.70 21.72 21.16 21.67 21.61 GA 25.59 25.59 25.59 25.59 25.59 25.59 -
[1] GALCERAN E, CARRERAS M. A survey on coverage path planning for robotics[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2013, 61(12): 1258-1276. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2013.09.004 [2] DENNISTON C, KROGSTAD T R, KEMNA S, et al. On-line AUV survey planning for finding safe vessel paths through hazardous environments[C]//IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Workshop. Porto: IEEE; 2018: 1-6. [3] KABA M D, UZUNBAS M G, LIM S N. A reinforcement learning approach to the view planning problem[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 5094-5102. [4] KRAININ M, CURLESS B, FOX D. Autonomous generation of complete 3D object models using next best view manipulation planning[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai: IEEE, 2011: 5031-5037. [5] LAKSHMANAN A K, MOHAN R E, RAMALINGAM B, et al. Complete coverage path planning using reinforcement learning for Tetromino based cleaning and maintenance robot[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 112: 103078. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103078 [6] JING W, GOH C F, RAJARAMAN M, et al. A computational framework for automatic online path generation of robotic inspection tasks via coverage planning and reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 54854-54864. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2872693 [7] WANG X D, SYRMOS V L. Coverage path planning for multiple robotic agent-based inspection of an unknown 2D environment[C]//2009 17th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation. Thessaloniki: IEEE, 2009: 1295-1300. [8] LIU Y C, SONG R, BUCKNALL R, et al. Intelligent multi-task allocation and planning for multiple unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) using self-organising maps and fast marching method[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 496: 180-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.05.029 [9] BEST G, FAIGL J, FITCH R. Online planning for multi-robot active perception with self-organising maps[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2018, 42(4): 715-738. doi: 10.1007/s10514-017-9691-4 [10] 贾庆轩, 陈钢, 孙汉旭, 等. 基于A*算法的空间机械臂避障路径规划[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010, 46(13): 109-115.JIA Q X, CHEN G, SUN H X, et al. Path planning for space manipulator to avoid obstacle based on A* algorithm[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(13): 109-115. (in Chinese) [11] 王洪斌, 郝策, 张平, 等. 基于A*算法和人工势场法的移动机器人路径规划[J]. 中国机械工程, 2019, 30(20): 2489-2496.WANG H B, HAO C, ZHANG P, et al. Path planning of mobile robots based on A* algorithm and artificial potential field algorithm[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 30(20): 2489-2496. (in Chinese) [12] 刘洪鹏, 赵文政, 刘银华, 等. 测量不确定度约束下的结构光检测视点规划方法[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2022, 28(4): 1079-1086.LIU H P, ZHAO W Z, LIU Y H, et al. View planning of structured light for free-form surfaces with control of measurement uncertainty[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 28(4): 1079-1086. (in Chinese) [13] BIRCHER A, KAMEL M, ALEXIS K, et al. Receding horizon path planning for 3D exploration and surface inspection[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2018, 42(2): 291-306. doi: 10.1007/s10514-016-9610-0 [14] MEYES R, TERCAN H, ROGGENDORF S, et al. Motion planning for industrial robots using reinforcement learning[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2017, 63: 107-112. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.03.095 [15] PAULL L, SETO M, LI H. Area coverage planning that accounts for pose uncertainty with an AUV seabed surveying application[C]//2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014: 6592-6599. [16] PRIETO F, BOULANGER P, LEPAGE R, et al. Automated inspection system using range data[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Washington: IEEE, 2002: 2557-2562. [17] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: an introduction[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 1998. [18] 安前松. 无人机三维覆盖路径规划及跟随制导研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018.AN Q S. Research on 3D coverage path planning and path following guidance of UAV[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese) -








 下载:
下载: