A Novel Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm of Auricular Conchal Morphology for Earphone Customization Design
-
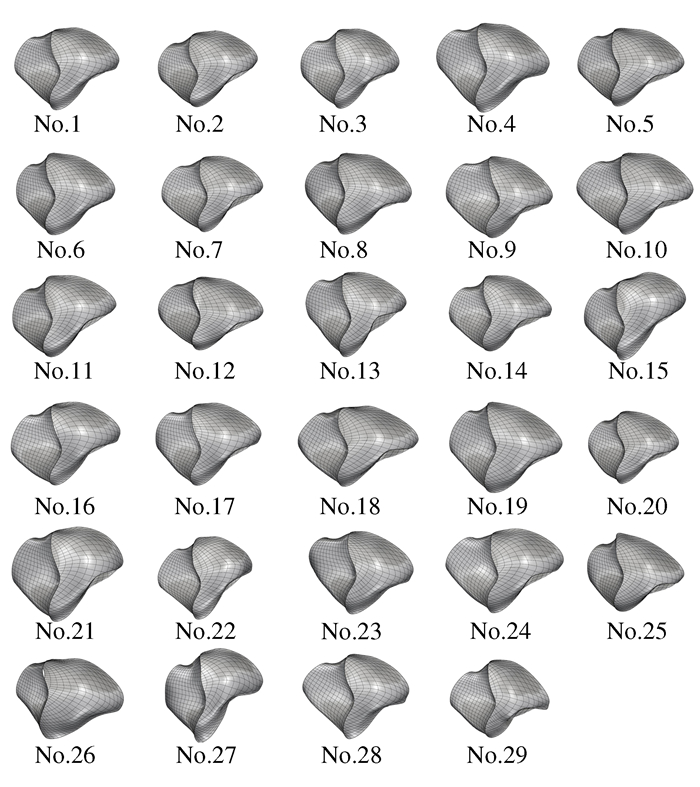
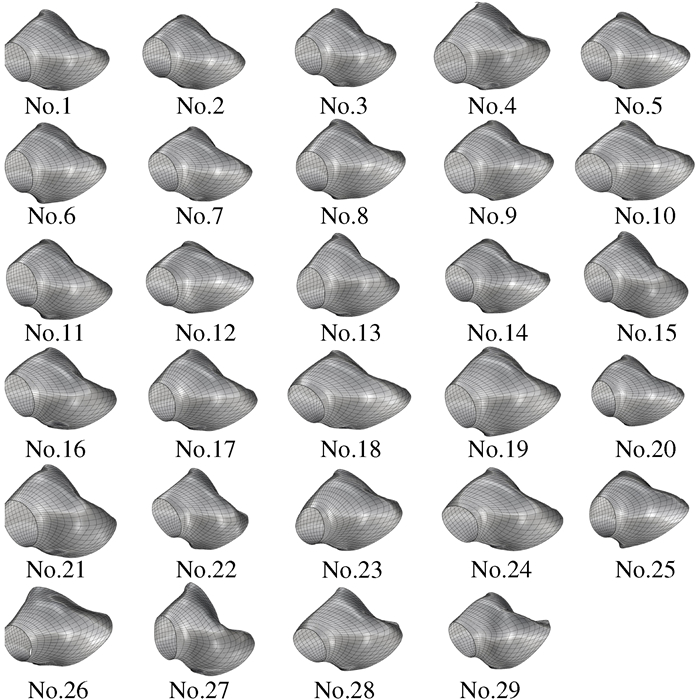
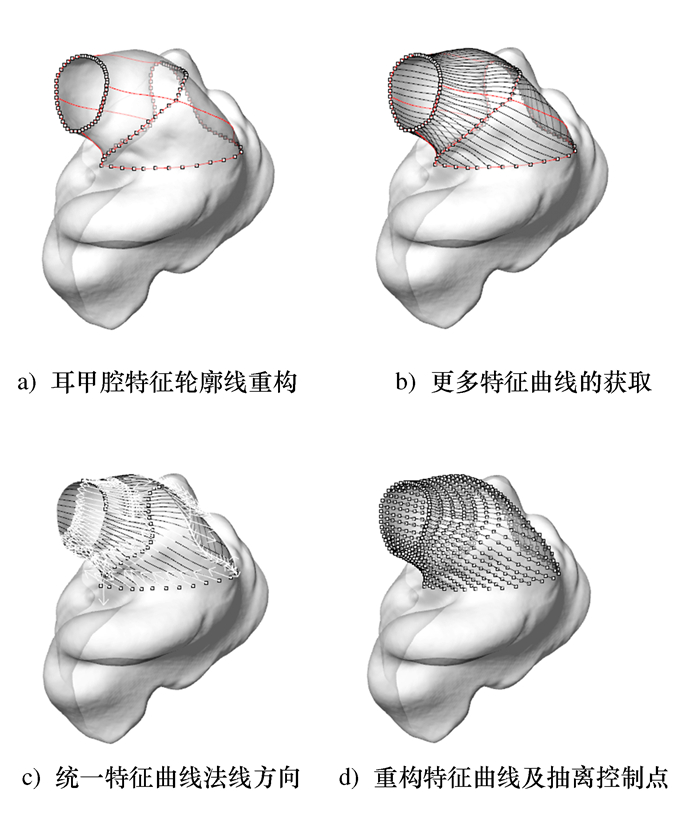
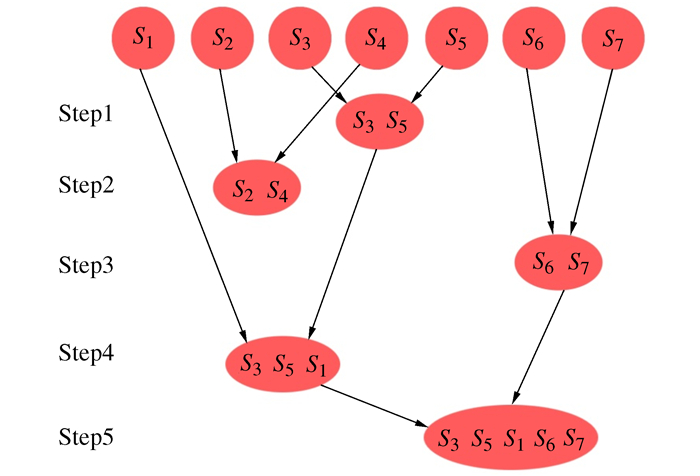
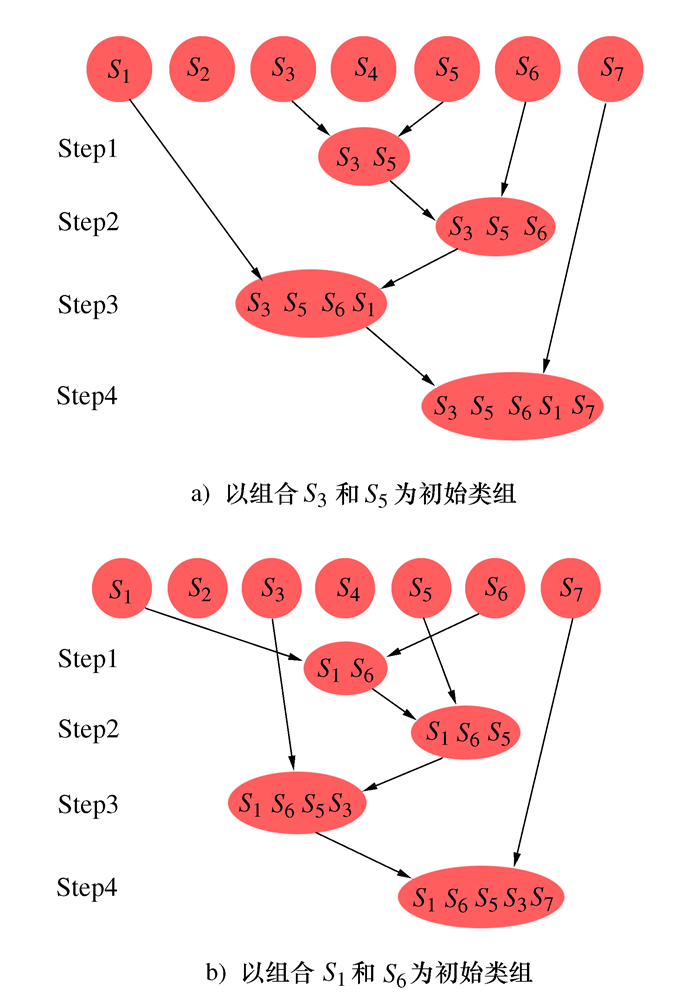
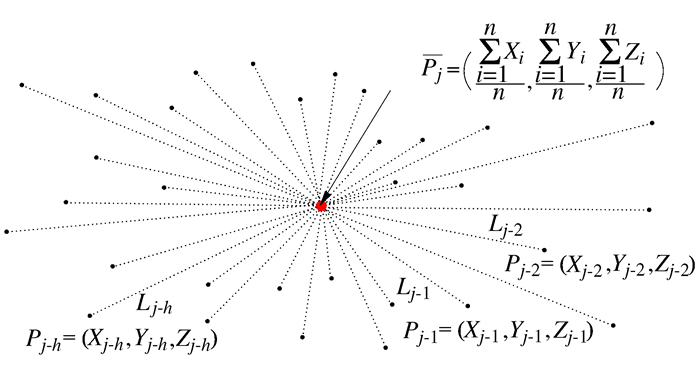
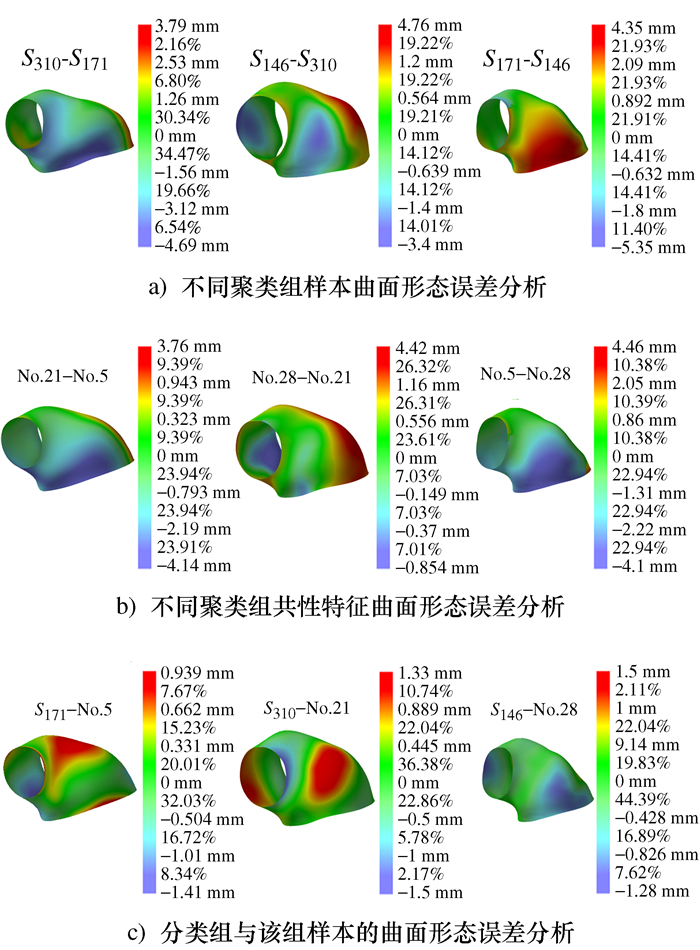
摘要: 为实现耳机大规模定制设计且满足用户使用舒适性需求的目标,提出人耳甲腔网格曲面自动重构的方法。将310个样本的耳甲腔网格曲面均重构为由795个型值点组成的NURBS曲面;进一步提出耳甲腔曲面形态层级聚类改进算法,并通过与传统分类算法结果的对比,论证改进算法的优势;其次依据分类的结果将人耳甲腔曲面形态分为29组别,从而构建针对耳机设计的耳甲腔共性特征曲面形态数据库,并通过曲面误差分析论证了数据库的可靠性;最终对耳机进行定制设计,提出基于有限元仿真分析的耳机佩戴舒适度的客观评价方法。Abstract: In order to realize the mass customization of wearable earphones, this paper firstly proposes a conchal mesh surface automatic reconstruction method and reconstructs the mesh surface of 310 samples into NURBS which consists of 795 points. Secondly, an improved hierarchical clustering algorithm for the conchal morphology is proposed, and the advantages of the algorithm are verified. Thirdly, the auricular conchal morphology is divided into 29 groups according to the algorithm, and the database of auricular conchal morphology for earphone design is constructed, and then the reliability of the database is verified. Finally, the earphones are customization-designed, and an objective fit evaluation method for earphone is proposed, which based on finite element simulation analysis.
-
表 1 各型值点阈值的设定
型值点 P1 P2 P4 P5 P6 P7a P7b P7c P7d P785 阈值 3.5 mm 3.6 mm 4.3 mm 4.6 mm 4.9 mm 4.8 mm 4.8 mm 4.9 mm 4.6 mm 5.5 mm 表 2 聚类结果
No 起始人数 分组人数 参数a 参数b 参数c 参数d 人数比例 1 308 66 0.84 0.40 1.32 2.95 21.4 2 242 32 0.80 0.44 1.54 2.86 10.4 3 210 30 0.73 0.37 1.24 2.16 9.7 4 180 22 0.71 0.35 1.55 2.17 7.1 5 158 21 0.89 0.42 1.35 2.61 6.8 6 137 15 0.89 0.46 1.52 3.42 4.9 7 122 15 0.95 0.46 1.63 2.90 4.9 8 107 12 0.91 0.47 1.76 3.10 3.9 9 95 12 0.68 0.37 1.25 2.15 3.9 10 83 10 0.89 0.43 1.60 2.70 3.2 11 73 7 0.98 0.50 1.64 2.88 2.3 12 66 6 0.97 0.44 1.66 2.54 1.9 13 60 5 0.90 0.44 1.46 2.84 1.6 14 55 4 0.94 0.49 1.74 3.00 1.3 15 51 5 1.00 0.50 1.69 2.78 1.6 16 46 4 1.11 0.56 1.85 2.95 1.3 17 42 5 0.75 0.46 1.89 2.97 1.6 18 37 4 0.80 0.42 1.53 2.57 1.3 19 33 5 1.11 0.57 2.29 3.21 1.6 20 28 4 1.13 0.55 2.14 2.95 1.3 21 24 3 0.87 0.45 1.83 2.44 1.0 22 21 3 1.05 0.54 2.23 3.02 1.0 23 18 2 0.84 0.42 1.58 2.09 0.6 24 16 2 0.88 0.41 1.60 3.14 0.6 25 14 3 0.93 0.45 1.68 2.54 1.0 26 11 2 0.75 0.40 1.82 1.82 0.6 27 9 2 0.84 0.43 2.02 2.02 0.6 28 7 2 0.93 0.45 1.68 1.68 0.6 29 5 2 0.48 0.31 1.65 1.65 0.6 人数 308 305 99.0 表 3 改进层级聚类算法与传统层级聚类算法的结果对比
聚类算法 分组数 参与样本 人数占比 参数a 参数b 参数c 参数d 改进层级聚类算法 29 305 99% 0.88 0.44 1.68 2.62 Single-linkage (Instastop) 24 159 52% 0.51 0.29 1.25 1.86 Single-linkage (Laterstop) 30 265 87% 0.71 0.35 1.37 2.32 Complete-linkage (Instastop) 27 185 61% 0.57 0.28 1.25 1.87 Complete-linkage (Laterstop) 43 299 98% 0.73 0.39 1.51 2.51 Mean linkage (Instastop) 27 205 67% 0.59 0.34 1.33 1.97 Mean linkage (Laterstop) 34 283 93% 0.67 0.38 1.57 2.31 Centroid linkage (Instastop) 27 215 70% 0.65 0.29 1.43 2.11 Centroid linkage (Laterstop) 40 293 96% 0.81 0.40 1.62 2.45 表 4 耳甲腔关键特征尺寸
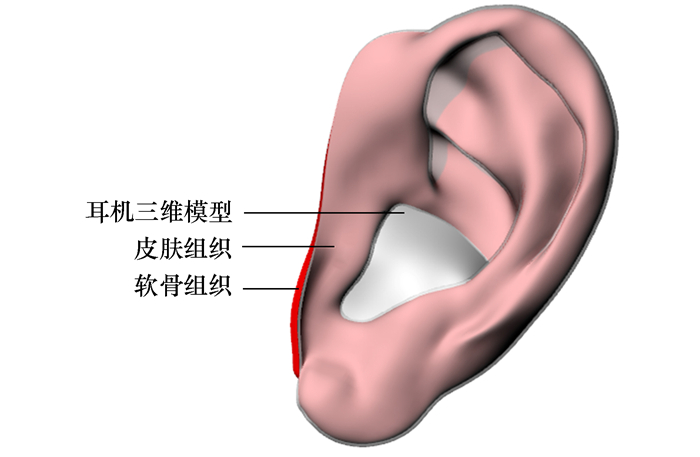
mm No P1P3 P3P5 P1P5 P7aP7b P7cP7d 1 17.13 16.57 16.25 9.27 7.09 2 15.40 15.73 15.18 9.15 7.12 3 16.87 14.93 15.55 8.95 7.15 4 19.30 16.88 18.14 9.86 7.97 5 16.65 15.84 16.85 9.49 7.25 6 17.37 15.92 16.99 9.61 6.71 7 16.01 15.14 14.68 9.21 6.91 8 17.37 16.36 18.09 9.44 7.19 9 17.58 15.05 16.63 9.73 7.55 10 17.39 16.35 17.50 9.69 7.77 11 17.14 17.08 16.19 10.22 7.67 12 15.55 15.06 16.28 9.35 6.99 13 18.09 16.31 15.24 9.56 6.96 14 15.96 16.21 16.70 8.71 7.14 15 17.11 17.53 14.76 7.51 7.35 16 17.16 17.36 16.57 10.01 8.19 17 17.34 16.87 16.41 9.43 7.17 18 16.87 17.94 18.03 9.86 7.86 19 19.27 17.73 19.02 10.26 7.70 20 15.47 14.41 14.69 8.27 6.50 21 19.50 18.34 16.49 11.28 8.87 22 17.47 16.08 14.16 9.49 5.90 23 17.72 14.82 16.79 8.93 6.87 24 17.20 17.25 16.63 9.47 8.03 25 16.69 14.83 17.41 9.21 6.94 26 16.74 17.14 19.34 8.67 7.29 27 19.48 17.35 15.34 10.12 7.19 28 18.17 15.00 16.30 8.82 7.18 29 16.61 14.18 16.63 8.83 6.52 表 5 耳廓组织及耳机材料特性
组织 材料类型 密度/
(kg·m-3)弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 皮肤 弹性 1 000 35 0.42 血管/神经 弹性 1 000 50 0.45 软骨 弹性 1 600 1 200 0.20 弹性尼龙 弹性 1 030 49.30 0.30 -
[1] Cai D C, Chen H L. Ergonomic approach for pillow concept design[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2016, 52:142-150 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.07.004 [2] Taifa I W, Desai D A. Anthropometric measurements for ergonomic design of students' furniture in India[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2017, 20(1):232-239 doi: 10.1016/j.jestch.2016.08.004 [3] Thai K T, Mcintosh A S, Pang T Y. Bicycle helmet size, adjustment, and stability[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2015, 16(3):268-275 doi: 10.1080/15389588.2014.931948 [4] Jee S C, Yun M H. An anthropometric survey of Korean hand and hand shape types[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2016, 53:10-18 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2015.10.004 [5] Kim S H, Kee D H. Classification and identification of Korean hand shapes based on anthropometric hand data analysis[J]. Journal of the Korea Safety Management and Science, 2012, 14(1):75-85 doi: 10.12812/ksms.2012.14.1.075 [6] Gutierrez A M J A, Galang M D, Seva R R, et al. Design-ing an improved respirator for automotive painters[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2014, 44(1):131-139 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2013.11.004 [7] Lee W, Jeong J, Park J, et al. Analysis of the facial measurements of Korean air force pilots for oxygen mask design[J]. Ergonomics, 2013, 56(9):1451-1464 doi: 10.1080/00140139.2013.816376 [8] Ellena T, Skals S, Subic A, et al. 3D digital headform models of Australian cyclists[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2017, 59:11-18 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2016.08.031 [9] Lacko D, Huysmans T, Vleugels J, et al. Product sizing with 3D anthropometry and k-medoids clustering[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2017, 91:60-74 doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2017.06.004 [10] Harih G, Dolšak B. Tool-handle design based on a digital human hand model[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2013, 43(4):288-295 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2013.05.002 [11] Harih G, Dolšak B. Comparison of subjective comfort ratings between anatomically shaped and cylindrical handles[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2014, 45(4):943-954 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003687013002640 [12] Gonzalez A G, Salgado D R, Moruno L G. Optimisation of a laparoscopic tool handle dimension based on ergonomic analysis[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2015, 48:16-24 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2015.03.007 [13] Harih G, Dolšak B. Recommendations for tool-handle material choice based on finite element analysis[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2014, 45(3):577-585 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003687013001555 [14] Dianat I, Nedaei M, Mostashar Nezami M A. The effects of tool handle shape on hand performance, usability and discomfort using masons' trowels[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2015, 45:13-20 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2014.10.006 [15] Lei Z P, Yang J Z, Zhuang Z Q. Contact pressure study of N95 filtering face-piece respirators using finite element method[J]. Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 2010, 7(6):847-861 doi: 10.3722/cadaps.2010.847-861 [16] Dai J C, Yang J Z, Zhuang Z Q. Sensitivity analysis of important parameters affecting contact pressure between a respirator and a headform[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2011, 41(3):268-279 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2011.01.007 [17] Ellena T, Subic A, Mustafa H, et al. The helmet fit index-an intelligent tool for fit assessment and design customisation[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2016, 55:194-207 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2016.02.008 [18] 孙海.层次聚类算法的改进[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2014 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D596483Sun H. The improvement of the hierarchical clustering algorithm[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2014(in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D596483 [19] Skals S, Ellena T, Subic A, et al. Improving fit of bicycle helmet liners using 3D anthropometric data[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2016, 55:86-95 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2016.08.009 [20] Pang T Y, Lo T S T, Ellena T, et al. Fit, stability and comfort assessment of custom-fitted bicycle helmet inner liner designs, based on 3D anthropometric data[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2018, 68:240-248 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2017.12.002 [21] Sun S P, Chou Y J, Sue C C. Classification and mass production technique for three-quarter shoe insoles using non-weight-bearing plantar shapes[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2009, 40(4):630-635 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2008.05.001 [22] Lee Y C, Wang M J. Taiwanese adult foot shape classification using 3D scanning data[J]. Ergonomics, 2015, 58(3):513-523 doi: 10.1080/00140139.2014.974683 [23] Baek S Y, Lee K. Statistical foot-shape analysis for mass-customisation of footwear[J]. International Journal of Computer Aided Engineering and Technology, 2016, 8(1-2):80-98 [24] Ellena T, Subic A, Mustafa H, et al. A novel hierarchical clustering algorithm for the analysis of 3D anthropometric data of the human head[J]. Computer-Aided Design and Applications, 2018, 15(1):25-33 doi: 10.1080/16864360.2017.1353727 [25] Ellena T, Mustafa H, Subic A, et al. A design framework for the mass customisation of custom-fit bicycle helmet models[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2018, 64:122-133 doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2018.01.005 [26] Godil A, Ressler S. Retrieval and clustering from a 3D human database based on body and head shape[J]. arXiv: 1105.2800, 2011 http://www.oalib.com/paper/4056954 [27] Zhu Z H, Ji X M, Gao Z, et al. A morphometric study of auricular concha in the population of young Chinese adults[J]. International Journal of Morphology, 2017, 35(4):1451-1458 doi: 10.4067/S0717-95022017000401451 [28] Zhao S C, Li D G, Liu Z Z, et al. Anthropometric growth study of the ear in a Chinese population[J]. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 2018, 71(4):518-523 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29169692 [29] Yu J F, Lee K C, Wang R H, et al. Anthropometry of external auditory canal by non-contactable measurement[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2015, 50:50-55 doi: 10.1016/j.apergo.2015.01.008 [30] Liu B S. Incorporating anthropometry into design of ear-related products[J]. Applied Ergonomics, 2008, 39(1):115-121 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003687007000087 [31] Jung H S, Jung H S. Surveying the dimensions and characteristics of Korean ears for the ergonomic design of ear-related products[J]. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 2003, 31(6):361-373 doi: 10.1016/S0169-8141(02)00237-8 [32] Lee W, Jung H, Bok I, et al. Measurement and application of 3D ear images for earphone design[J]. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, 2016, 60(1):1053-1057 doi: 10.1177/1541931213601244 [33] Sforza C, Grandi G, Binelli M, et al. Age-and sex-related changes in the normal human ear[J]. Forensic Science International, 2009, 187(1-3):110.e1-110.e7 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0379073809000966 [34] Coward T J, Scott B J J, Watson R M, et al. Laser scanning of the ear identifying the shape and position in subjects with normal facial symmetry[J]. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 2000, 29(1):18-23 doi: 10.1016/S0901-5027(00)80117-4 [35] Barut C, Aktunc E. Anthropometric measurements of the external ear in a group of Turkish primary school students[J]. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 2006, 30(2):255-259 doi: 10.1007/s00266-005-0182-1 [36] Purkait R, Singh P. Anthropometry of the normal human auricle:a study of adult Indian men[J]. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 2007, 31(4):372-379 doi: 10.1007/s00266-006-0231-4 [37] 朱兆华, 吉晓民, 高瞩, 等.人耳曲面特征点提取与形状分类方法研究及应用[J].机械科学与技术, 2018, 37(3):409-417 http://journals.nwpu.edu.cn/jxkxyjs/CN/abstract/abstract6967.shtmlZhu Z H, Ji X M, Gao Z, et al. An approach to design earphones by extracting characteristic points and classifying shape of auricular conchae[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2018, 37(3):409-417(in Chinese) http://journals.nwpu.edu.cn/jxkxyjs/CN/abstract/abstract6967.shtml [38] 陈新泉, 周灵晶, 刘耀中.聚类算法研究综述[J].集成技术, 2017, 6(3):41-49 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3135.2017.03.004Chen X Q, Zhou L J, Liu Y Z. Review on clustering algorithms[J]. Journal of Integration Technology, 2017, 6(3):41-49(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-3135.2017.03.004 [39] 靳延安, 刘行军.一种改进的层次聚类算法[J].武汉理工大学学报信息与管理工程版, 2011, 33(6):883-886, 912 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whqcgydxxb201106009Jin Y A, Liu X J. An improved hierarchical clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Information & Management Engineering), 2011, 33(6):883-886, 912(in Chinese) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whqcgydxxb201106009 [40] 周世兵.聚类分析中的最佳聚类数确定方法研究及应用[D].江苏无锡: 江南大学, 2011 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10295-1012278977.htmZhou S B. Research and application on determining optimal number of clusters in cluster analysis[D]. Jiangsu Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2011(in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10295-1012278977.htm [41] 李彩云.基于密度的改进型层次聚类算法研究[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2016 http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1016723021.htmLi C Y. Research on improved hierarchical clustering algorithm based on density[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University (in Chinese) http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10730-1016723021.htm [42] 曾衍钧, 许传青, 杨坚, 等.软组织的生物力学特性[J].中国科学(G辑), 2003, 33(1):1-5 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cg200301001Zeng Y J, Xu C Q, Yang J, et al. Biomechanical properties of soft tissues[J]. Science in China Series G:Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2003, 46(3):284-290 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cg200301001 [43] 周先连, 王有朝, 王成焘.面中部牵张成骨有限元研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2004, 21(2):292-296 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2004.02.031Zhou X L, Wang Y Z, Wang C T. Three-dimensional finite element study on middle face advancement with distraction osteogenesis[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 21(2):292-296(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2004.02.031 [44] 冉令鹏, 王崴, 丁日显, 等.舒适性耳机半参数化设计优化研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2015, 23(6):646-650 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2015.06.019Ran L P, Wang W, Ding R X, et al. The optimization of comfortable earphone designed by the method of semi-parametric[J]. Journal of Audiology and Speech Pathology, 2015, 23(6):646-650(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2015.06.019 -








 下载:
下载: