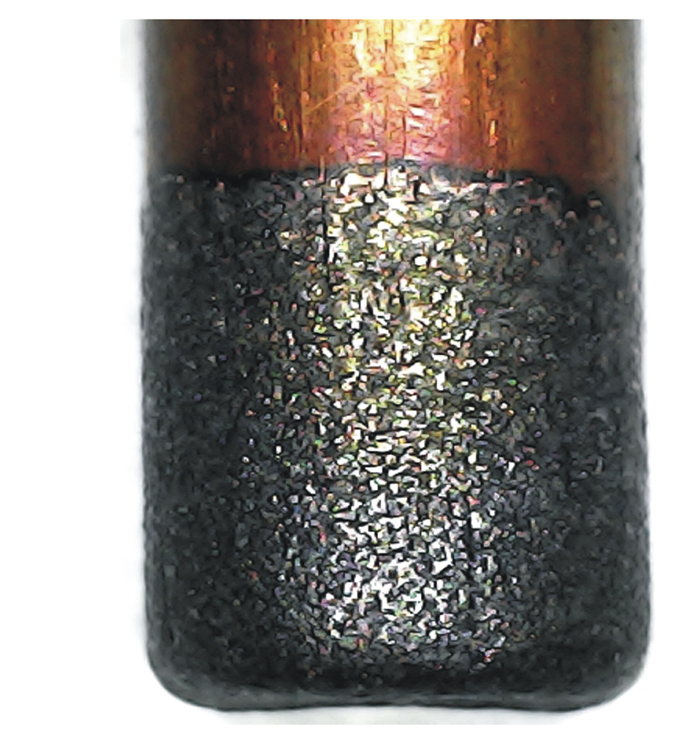
Experimental Study on Multi-objective Optimization of EDM Small Hole Machining for TC4 Titanium Alloy
-
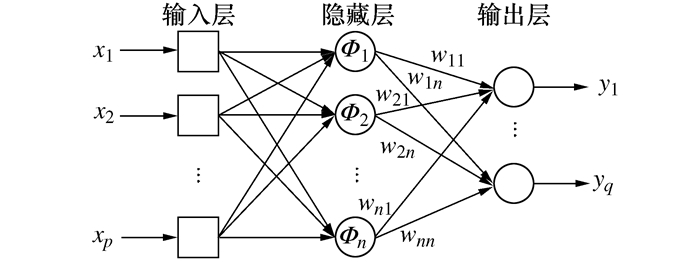
摘要: 为提升电火花加工TC4钛合金的表面加工质量和加工效率, 选取紫铜圆柱电极开展TC4钛合金电火花小孔加工试验, 采用正交试验法, 以电极相对损耗率、表面粗糙度、工件材料去除体积为工艺指标, 分析峰值电流、维持电压、放电脉宽对工艺指标的影响重要性。采用RBF(Radial basis function)神经网络对已有试验数据进行训练, 建立放电参数与工艺指标之间的数学预测模型。以该预测模型为适应度函数, 将遗传算法与Skyline选择算法结合进行多目标优化仿真, 得到最佳工艺指标, 最后开展多目标优化验证试验。结果表明: 当峰值电流为14 A、维持电压39 V/42 V、放电脉宽102 μs/108 μs时能够取得最优的加工结果, 优化值与试验值误差较小。
-
关键词:
- 电火花加工 /
- RBF神经网络 /
- 遗传算法 /
- Skyline选择算法 /
- 多目标优化
Abstract: To improve the surface machining quality and machining efficiency of TC4 titanium alloy in EDM (Electrical discharge machining), the copper cylindrical electrode was selected to carry out EDM small hole machining experiment of TC4 titanium alloy. The orthogonal experiment method was adopted. Taking the relative electrode wear rate, surface roughness and material removal volume of workpiece as optimization objectives, the influences of the peak current, discharge voltage and discharge pulse width on the optimization objectives were analyzed. RBF (Radial basis function) neural network was used to train with the experimental data, and the prediction model between the discharge parameters and the optimization objectives was established. Taking the prediction model as the fitness function, the multi-objective optimization simulation was carried out by combining the genetic algorithm with the Skyline selection algorithm, and the optimal technical index was obtained. Finally, the multi-objective optimization verification experiment was carried out. The results show that when the peak current is 14 A, the maintenance voltage is 39 V/42 V, and the discharge pulse width is 102 μs/108 μs, the optimal machining results can be obtained, and the error between the optimal value and the experimental value is small. -
表 1 钛合金电火花小孔加工放电参数
参数 描述 电极材料 紫铜 工件材料 TC4钛合金 极性 负极性 工作液 煤油 电极直径D/mm 3 加工时间t/min 15 表 2 放电加工正交试验
水平 A B C 1 14 30 50 2 18 40 100 3 22 50 150 表 3 放电加工正交试验结果
序号 峰值电流/A 维持电压/V 放电脉宽/μs 电极相对损耗率/% 表面粗糙度/μm 工件材料去除体积/mm3 1 14 30 50 9.321 1.955 5.987 2 14 40 150 7.078 3.795 7.095 3 14 50 100 10.786 3.121 6.208 4 18 30 150 7.366 3.164 9.091 5 18 40 100 19.093 2.725 6.430 6 18 50 50 19.246 2.721 7.539 7 22 30 100 16.016 2.573 4.878 8 22 40 50 16.778 2.761 10.643 9 22 50 150 16.237 2.988 6.874 K1 9.060 10.901 15.115 K2 15.235 14.316 15.298 K3 16.344 15.423 10.227 极差R1 7.284 4.522 5.071 K4 2.957 2.564 2.479 K5 2.870 3.094 2.806 K6 2.774 2.943 3.316 极差R2 0.183 0.151 0.837 K7 6.430 6.652 8.056 K8 7.687 8.056 5.839 K9 7.465 6.874 7.687 极差R3 1.257 1.404 0.369 表 4 神经网络模型试验值与预测值对比
序号 峰值电流/A 放电电压/V 放电脉宽/μs 电极相对损耗率/% 表面粗糙度/μm 工件材料去除体积/mm3 试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 1 14 30 100 9.7 10.9 2.462 2.409 5.765 5.085 2 14 30 150 7.5 8.8 2.665 2.608 5.987 5.252 3 14 50 150 5.2 4.8 5.213 4.964 6.430 6.153 4 22 30 150 17.2 15.5 4.367 4.005 8.426 8.911 表 5 多目标优化结果与试验值对比
序号 峰值电流/A 放电电压/V 放电脉宽/μs 电极相对损耗率/% 表面粗糙度/μm 工件材料去除体积/mm3 试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 1 14 39 102 5.761 6.742 1.985 2.236 5.024 4.845 2 14 42 108 6.453 7.231 1.982 2.334 4.847 4.213 -
[1] PRADHAN B B, MASANTA M, SARKAR B R, et al. Investigation of electro-discharge micro-machining of titanium super alloy[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 41(11-12): 1094-1106 doi: 10.1007/s00170-008-1561-y [2] ZHANG S F, ZHANG W C, LIU Y, et al. Corrigendum to Study on the gap flow simulation in EDM small hole machining with Ti alloy[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 2017: 7961763 [3] 王续跃, 胡辉, 梁延德, 等. 钛合金小孔电火花加工有限元仿真研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2013, 24(13): 1738-1742+1748 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2013.13.008WANG X Y, HU H, LIANG Y D, et al. Finite element simulation of small-hole on titanium alloy drilled by EDM[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 24(13): 1738-1742+1748 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2013.13.008 [4] 马文宇, 何云, 李志慧, 等. 整硬麻花钻刃型结构对加工钛合金切削性能的影响[J]. 硬质合金, 2021, 38(2): 133-140 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZHJ202102010.htmMA W Y, HE Y, LI Z H, et al. Influence of edge structure of solid carbide twist drill on cutting performance of machining titanium alloy[J]. Cemented Carbide, 2021, 38(2): 133-140 (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZHJ202102010.htm [5] 李明辉. 电火花加工理论基础[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1989LI M H. Fundamentals of EDM theory[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1989 (in Chinese) [6] 宗晓明, 高飞, 权超健, 等. GCr15轴承钢电火花线切割工艺参数优化[J]. 轴承, 2020(7): 9-14 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CUCW202007003.htmZONG X M, GAO F, QUAN C J, et al. Optimization of WEDM process parameters for GCr15 bearing steel[J]. Bearing, 2020(7): 9-14 (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CUCW202007003.htm [7] SHARMA N, RAJ T, JANGRA K K. Parameter optimization and experimental study on wire electrical discharge machining of porous Ni40Ti60 alloy[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2017, 231(6): 956-970 doi: 10.1177/0954405415577710 [8] 王蕾, 郭鲁荻, 戴恩成. 基于灰色关联分析法的GH4169合金电火花线切割加工参数优化[J]. 航空精密制造技术, 2020, 56(2): 31-34 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2020.02.008WANG L, GUO L D, DAI E C. Parameter optimization of GH4169 alloy in WEDM based on gray correlation[J]. Aviation Precision Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 56(2): 31-34 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5451.2020.02.008 [9] 王天姝. 钛合金电火花沉积涂层微观组织及工艺优化研究[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2019WANG T S. Study on microstructure and process optimization of electro-spark deposition coating on Titanium alloy[D]. Dalian: Dalian Jiaotong University, 2019 (in Chinese) [10] 李兴莘, 张靖, 何宇, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的微电网多目标优化调度[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2021, 37(3): 1-7 doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1672-0792.2021.03.001LI X S, ZHANG J, HE Y, et al. Multi-objective optimization dispatching of Microgrid based on improved particle swarm algorithm[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2021, 37(3): 1-7 (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1672-0792.2021.03.001 [11] ASSARZADEH S, GHOREISHI M. Neural-network-based modeling and optimization of the electro-discharge machining process[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2008, 39(5-6): 488-500 doi: 10.1007/s00170-007-1235-1 [12] 关书怀, 沈艳霞. 基于粒子群优化径向基函数神经网络的电力负荷预测[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2021, 40(5): 128-131 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGQJ202105036.htmGUAN S H, SHEN Y X. Power load forecasting based on PSO RBF-NN[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2021, 40(5): 128-131 (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGQJ202105036.htm [13] 丁小艳, 程俊, 丁德林. 基于神经网络和遗传算法的电沉积Ni-TiB2复合镀层工艺参数优化[J]. 电镀与精饰, 2020, 42(11): 20-24 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJI202011005.htmDING X Y, CHENG J, DING D L. Optimization of process parameters of electrodepositing Ni-TiB2 composite coating based on neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Plating & Finishing, 2020, 42(11): 20-24 (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DYJI202011005.htm [14] MARTÍNEZ-ALVARADO R, ALBA G G H, LEYVA- BRAVO J, et al. Radial basis function neural network for modelling an electrical discharge machining drilling process[C]//2018 IEEE International Autumn Meeting on Power, Electronics and Computing (ROPEC). Ixtapa: IEEE, 2018: 1-6 [15] 王海艳, 王倩. 支持偏好度动态适应的Skyline服务选择方法[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 42(11): 91-96 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201411017.htmWANG H Y, WANG Q. Skyline service selection approach with dynamic adaptation to user preference degree[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(11): 91-96 (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201411017.htm [16] HEIDARI M, EMADI S. Services composition in multi-cloud environments using the skyline service algorithm[J]. International Journal of Engineering, 2021, 34(1): 56-65 -








 下载:
下载: